Search the Community
Showing results for tags 'relative work'.
Found 11 results
-
Hi all, I'm wondering what the regulatory requirements are for relative work in different countries (e.g. in the UK if qualified under the BPA, you need FS1) and specifically, what the requirements are in Spain and Portugal. In Spain and Portugal, is some equivalent of FS1 required of it you have someone experienced who wants to start to show you things, can you go with?
- 3 replies
-
- relative work
- fs1
-
See more
Tagged with:
-
Skydive Fretoy is the closest skydiving center from Paris. Come fly with us We're offering tandem skydiving, skydiving lessons & solo jumps for proflyers. We're opened every weekend starting from Friday noon and during weekdays according to our opening schedule. Please contact us for further information and reservation at +33 3 44 43 68 39. Visit also our website. Blue sky! The Skydive Fretoy Team
-
(This article was first published in Parachutist magazine under the title "The ABCs of 4-Way", and has been published with consent of the author) 4-way is a group activity, so jumpers should learn it as a team. This article offers advice for doing just that. As such, it is geared toward jumpers new to 4-way, but you don’t have to be a student to be “new to 4-way.” Jumpers with experience in other disciplines like freeflying, canopy RW, or skysurfing can be new to 4-way. Even jumpers with experience on big-ways can be new to 4-way flying. Before you read another word, remember this: Learning 4-way is a gradual process. You have to start with simple drills and work your way up, adding to your skill set as you go. The skills you learn in the beginning will be useful down the road, even in the most complicated block moves. So, learn 4-way correctly from the get-go. Here, then, are suggestions for learning 4-way flying techniques from the ground up, so to speak. Train with video.No team should jump without video. Jumpers might have to swallow a little pride the first time they see their screw-ups on video, but it’s well worth it. Video helps jumpers identify and correct problems before they become bad habits, and it saves money. What might have taken a couple hundred jumps to learn in the pre-video days, jumpers today can learn in 20 or 30 jumps. Camera flyers deserve every penny put toward their slots. Match fall rates and fly no-contact.A team’s first few practice jumps should be devoted to finding a compatible fall rate and basic body control. Both can be accomplished on the same jump. Here is a good drill: Launch a 2-way with the other two jumpers exiting as close as possible.Build a Star then drop grips and try to stay level with the formation and in your slots. Adjust your fall rates to match that of the fastest falling jumper. Jumpers who float after adjusting their body position should wear weights on the next jump. If three of the jumpers are arching the whole time to stay down with the fastest-falling jumper, that jumper should probably wear a looser jumpsuit on the next jump. The rest of the jumpers should wear slick suits. It might take several jumps to get fall rates and body control worked out, but it is important. You can’t do 4-way if you can’t stay level and in your slot. Practice turning in place.After jumpers learn to fly no-contact and fall at the same rate, they can move on to turning in place. Here is a drill: From a no-contact Star, two jumpers across from each other turn 90 degrees (either direction) while the other two jumpers stay put (facing in). Fly these positions while staying in your slots. Try to stay close enough so you could take grips if you wanted to. After a designated jumper gives the “key,” go back to the no-contact Star. (A “key” is a signal to break for the next point.) Make two or three jumps doing this drill, then two or three more, this time substituting 360-degree turns for the 90-degree ones. Practice single formations.After teams can fly no contact and turn in place, they can start on randoms(single formations) selected from the 4-way dive pool *. * The 4-way dive pool is published in USPA’s Competition Manual. The dive pool is used for parachuting competitions around th world and is agreed upon by the IPC (International Parachuting Commission) at the beginning of each year. In the 4-way dive pool, single formations are called “randoms.” As of this writing, there are 16 randoms in the dive pool. Teams should start with simple randoms, where jumpers are facing in and nobody moves more than 90 degrees to go to the next formation. The following illustration shows a sequence of three simple randoms. Jumpers perform the sequence in the order shown (Star-Satellite-Zipper) then repeat the sequence. (For more challenging flying, a team can build the Zipper before the Satellite.) (Note: The Zipper is not a formation in the current 4-way dive pool but it is a good tool for learning how to stay level.) Techniques to practice while performing this sequence include: Flying with little tension on grips. Paying attention to the keys. If you can’t see the person giving the key, look into the eyes of a jumper who can see the key – it will tell you a lot! Moving smoothly and in control to the next point. Stopping the move and flying level before taking grips. Once teams can do drills like the one above, you can move on to more difficult randoms.But they shouldn’t do so without proper coaching. With all the formations in the dive pool, new teams can easily get lost in a fog deciding how to transition (move from one point to the next). What might look like a good move for one jumper might hinder the moves of other jumpers. Dive engineering is not rocket science, but it requires experience to see the most efficient moves for each jumper. Let a coach map out the moves so the team can focus on performance. Practice exits.The success of any 4-way jump depends on a solid exit. New teams should dedicate several jumps to exit practice. They should start with simple exits where all jumpers can look into the center. And they should check with a coach before they go up to make sure they are doing it correctly. A good way to focus only on exits is to jump at a lower altitude, say 6,000 feet so there is little time for anything but the exit.With 16 randoms and 22 block sequences in the 4-way dive pool, there are 38 possible exits. But the same principle applies to each. Jumpers exit as one stable unit by presenting themselves and the formation to the relative wind*. The formation should ride smoothly on the relative wind without buffeting or creating undue tension on grips.* Relative Wind is the air coming at you from the direction you are falling. On exit, the prop blast is the first type of relative wind you encounter, although this lasts only a second or two. As you fall away from the plane, the relative wind comes more and more from straight up from the ground. Learn your slots.On a 4-way team, there are four slots: Point, Outside Center, Inside Center and Tail. The camera flyer, the fifth (and invaluable) member of the team, does not turn points with the team, so the camera position is not discussed here. (But be good to your camera flyer – you can’t do without video!) The Point typically flies in the “front floater” position on the high end of the formation as it leaves the plane. He or she is responsible for launching out and up on exit. The Point usually makes bigger moves, especially in the block sequences. Typically, this slot is given to the jumper who is better at the longer moves. The Outside Center flies in the “middle floater” position and works with the Inside Center to build the center of most formations. The Outside Center also catches the Point in some block moves. The Inside Center exits from inside the door across from the Outside Center. It might appear that this is an easy position since the jumper is often facing out, but timing and body position are important. The Inside Center exits “with” the group and normally presents his or her chest to the relative wind. If the relative wind catches them in the back, they can fold underneath the formation. On some teams, the Outside Center gives the count and keys transitions. On other teams, the Inside Center gives the count and keys the next point. For this reason, both the centers should be able to lead the skydive and fly their slots at the same time. The Tail usually flies in the “rear floater” position and is responsible for anchoring the formation down as it flies off the plane. Sometimes it appears that the Tail exits early. Whether this is true is up for debate. The important things are timing and placement. As long as the Tail stays low on exit, the formation has a better chance of flying smoothly on the relative wind. Learn to fly on the hill.Experienced 4-way teams transition to the second point right off the plane while the formation is semi-upright relative to the ground. This is called flying “on the hill.” New teams should not try to transition on the hill until they can consistently pull off good exits. Even then, they should transition to simple formations where not much movement is involved. Also, teams should not try block sequences on the hill until they can consistently transition to single formations. Here is a simplified look at hill flying. The exit is the first part of hill flying. Moving to the next point is the next part. As long as the exit formation flies stable on the relative wind, you can make the same moves on the hill that you make when the formation is falling at terminal velocity. You just have to put more punch into some moves because the air is a little “mushy” (meaning the formation hasn’t yet reached terminal velocity). Probably the hardest part about hill flying is learning to ignore the fact that it seems like you’re sometimes standing on your head (or vice versa) when making your move. In Summary:If you can perform the techniques discussed in this article, you’re a darn good skydiver. But you have so much more to look forward to, like block sequences where you fly with piece partners. But don’t jump ahead just yet. Piece flying injects a completely new set of dynamics into 4-way flying and builds upon the fundamentals discussed in this article. So learn the basics first. Learn them as a team. Find a compatible fall rate before you practice randoms. Learn how to make smooth, controlled moves. Set aside jumps for practicing nothing but exits. Learn all the randoms in the dive pool. Then keep practicing. Spend an entire season doing randoms if necessary. Then you will be ready move on to the block sequences. Don’t expect miracles overnight, but do expect rewards for hard work. It might be weeks before your team has a breakthrough, but when you do, it will be exhilarating! The light will come on for the team all at once - you’ll see it in each other’s eyes in freefall. You’ll feel it in the rhythm of the skydive. And, most important, you’ll see it in your score!
-
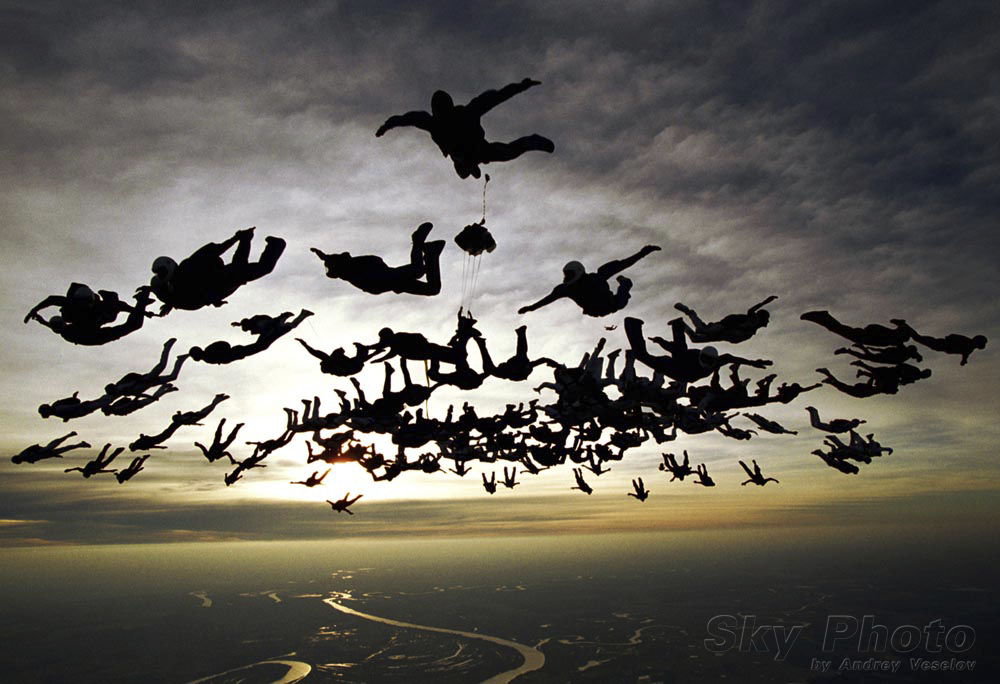
Image by Andrey VeselovThis article is a continuation of my previous article “Diving and Tracking Safety on Large Formation Skydives”. Some of that article is repeated here because maximum separation under canopy cannot be achieved without proper breakoff and tracking. On any skydive, it is critical that jumpers keep their heads on a swivel at all times. Nowhere is this more important than large formation skydives where separation is paramount and there is no place for canopies weaving in and out of traffic or front-riser spiraling below other jumpers and cutting them off in the landing area. A few years ago, Kate Cooper-Jensen and other big-way organizers compiled what they called “Rules of the Sky” for canopy piloting on big-way formation skydives. Cooper-Jensen makes sure that everybody knows about these rules at every big-way event she runs. This article reiterates those rules and provides a few additional rules a jumper must follow from the time he breaks off until he opens. Let’s start with responsibilities during breakoff and tracking.At breakoff, jumpers turn and track with their designated tracking groups. Breakoff turn directions should have already been established in the dirt dive to avoid collisions. But turn direction is one thing; how far to turn is another. Jumpers facing the center of the formation turn a full 180 degrees at breakoff. A jumper who is already facing, say, 45 degrees away from the center of the formation turns only about 135 degrees. Jumpers track with their groups for at least five seconds, staying level with their tracking leaders then fanning out a few degrees from the center until the designated opening altitude for their group. A “flat track” is required and absolutely no steep (or “dive”) tracking is allowed! If a jumper goes low, he moves off to the side, assumes a slow fall rate, and tries to get above the formation until the outer wave breaks off, at which time he turns and tracks as far as he can until 2500 feet. Jumpers on the outside of the formation break off first, track the furthest, and open the lowest. Jumpers in the middle break off next and track as far as they can until time to open (at the highest altitude on the load). Jumpers in the base ring track the least distance and open at a low altitude like the outer groups. These staggered openings make it is easier for jumpers to see each other and fly their canopies. Imagine how congested the skies would be if everybody on a 100-way opened at the same altitude. Image by Andrey VeselovAs a jumper tracks, he scans the sky in front, below, and on either side. It is his responsibility to watch out for jumpers below. It is also his responsibility to check the sky directly above before he waves off. If another jumper appears directly above or below as he waves off, the jumper can continue tracking to get out of the way. Once a jumper is under a good canopy, the first thing he must do is grab his rear risers and be ready to yank down on a riser if another canopy is coming at him. The general rule is to yank down on the right rear riser if another canopy is approaching directly from the front. If a canopy is coming from another direction, however, say, from the right, it is obvious that the left rear riser should be used. Once the jumper is absolutely sure he is clear of other jumpers, he can collapse his slider, flip up his visor (if applicable), and release his brakes. However, jumpers on large formation loads are normally not permitted to remove booties under canopy. The jumper is now ready to navigate his canopy alongside other canopies in his group on their way to the landing area. Here are the “Rules of the Sky” that big-way jumpers must follow under canopy:Know the recommended canopy wing loading for the event. While not set in stone, a wing loading between 1.25 and 1.75 is typically recommended on large formation skydives so that all canopies will be flying at roughly the same speed. Weights increase a canopy’s wing loading and jumpers should already know if they can safely fly their canopies with the additional weight. Inspect a map of the DZ and landing areas prior to jumping. Know the “outs” and alternate landing areas. This applies mostly to visiting jumpers unfamiliar with the DZ. Know the designated landing direction and landing areas. At most DZs, jumpers follow a left-hand landing pattern unless the spot and wind direction make it impossible to do so. A mandatory landing direction is often assigned. If separate landing areas have been assigned to different sections of the formation, a jumper must follow the same pattern as his landing group. Note: Downwind or crosswind landings may be required by the predetermined landing direction or because of a wind shift after the first canopy lands. Jumpers should already possess the skills necessary to land their canopies crosswind or downwind. Do not cross over into the pattern of another group. If the spot is long, try to make it back to the designated landing area unless doing so would interfere with other jumpers trying to get to their landing areas. In this case, pick an alternate landing area before reaching 1000 feet. Enter the group’s landing pattern around 1000 feet. Follow but stay off to the side of other jumpers entering the landing pattern. Never fly directly behind another canopy. The leading jumper can’t see you and the depressurized air behind the leading canopy can cause your canopy to collapse. Make the final turn between 300 and 500 feet and make no more turns after that. On final approach, turn no more than 90 degrees and never perform S-turns, spiral or hook turns, or fly in deep brakes. This includes camera personnel, organizers, and DZ staff. After landing, turn around while stowing breaks, etc. This allows you to get out of the way of jumpers landing behind you. If the landing area is congested, move off to the side as quickly as possible while watching out for other jumpers trying to land. If landing off the DZ, gather in groups and walk together to the nearest road. If required, check in with the group’s/plane’s designated person. This is especially important if jumpers have landed off the DZ. ConclusionSafety starts with the attitudes and the actions of each and every one of us. While it is perfectly acceptable to demonstrate confidence and experience, it is never acceptable to show off with a blatant disregard for the rules and the safety of others. On the other end of the spectrum, it is never acceptable for a jumper to put himself on a load or in a slot that he is not experienced enough to handle. At one extreme there is over-confidence, at the other, lack of experience. Either one can kill. Reading fatality reports is a sad undertaking but it also makes us angry – angry that the poor judgment of a few puts the rest of us at risk and gives our sport bad press – angry that needless injuries and deaths still occur – and, finally, angry that dear friends had to make the ultimate sacrifice in order for the rest of us to learn. Big-way organizers can only do so much. They can invite the most experienced skydivers in the world, but if just one skydiver doesn’t follow the rules, the results can be fatal. So let’s police ourselves and follow the rules, not just on big-ways, but each and every time we strap on a rig or get a student ready for his first skydive. This sport is a heckuva lot of fun when we do.
-
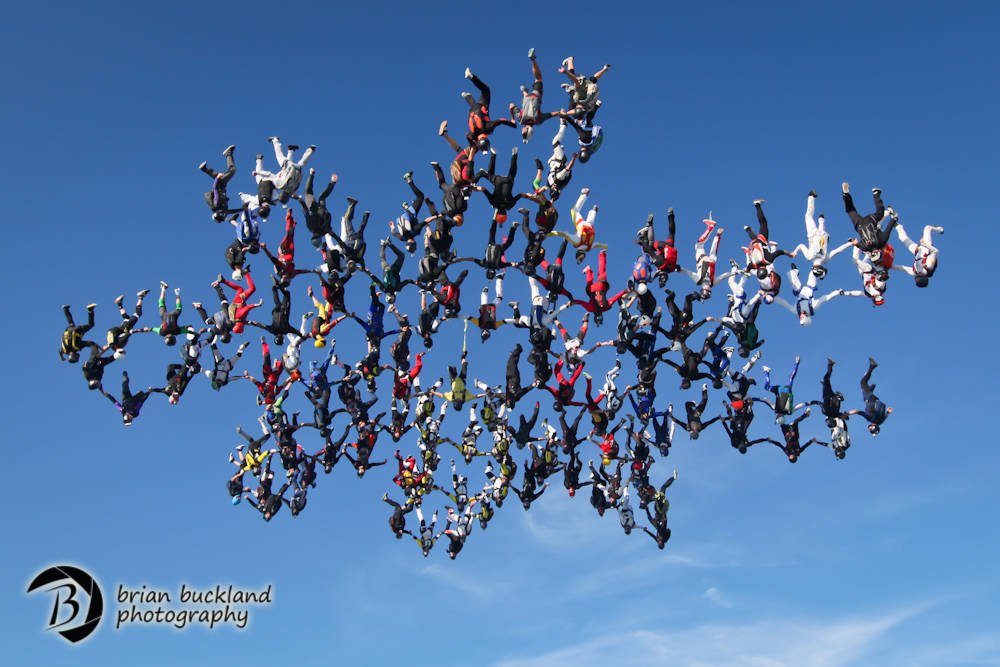
Image by Brian BucklandBy Ed Lightle This is the first of two articles geared toward safety on big-way formation skydives. This article deals mostly with the freefall part of the skydive whereas the second article “Canopy Safety on Large Formation Skydives” deals mostly with safety under canopy. To get the most benefit, it is recommended that you read both articles. In Formation Skydiving, hundreds of big-ways are completed every year without incident. This is a testament to both the skill level of today’s formation skydivers and the screening process utilized by big-way organizers. To qualify for most big-way events, a participant must obtain the recommendation of a big-way plane captain or organizer and must have recently participated in a big-way camp or big-way event. Organizers take safety seriously. A safety violation on a big-way, whether at a training camp or on a big-way attempt, will get a jumper benched when an honest learning mistake might not. Diving and tracking on big-ways are special areas of concern. With longer diving and tracking times and more jumpers in the air, big-ways naturally increase the risk of a freefall collision. But this risk can be eliminated if jumpers use good common sense and think safety on each and every jump. Here are some tips that can help. Watch Jumpers Ahead of You While DivingAs soon as a diver leaves the plane and gets squared away, he must identify the base and the jumpers who will be docking ahead of him in the formation. He must keep them in sight while he dives, stops, sets up and moves in to dock. He should constantly scan the sky in front of him, starting from the base and extending all the way out to the person he will be docking on. He should keep an eye out for camera flyers as well. Because several divers are heading to the same sector of the formation, each diver must follow a straight line from the plane to the area outside the formation where he wants to be stopped and ready to follow jumpers ahead of him into his slot. A jumper should never dive directly behind another diver in case the leading diver comes out of his dive early. The trailing diver should always stay a few feet off to the side. Don’t ZigzagIf a diver flares (comes out of his dive) early, he should not zigzag from side to side to bleed off altitude. If he does, he risks being hit by jumpers who are diving behind him. To bleed off altitude at this point, he should either get back into his dive (if he has a lot of distance to make up) or assume a fast fall position while keeping jumpers ahead of him in view. Get to the Red Zone on TimeAnother area of concern is getting down to the red zone in time. (The red zone is the area around and outside the formation where jumpers have stopped their dives and are lined up and moving straight ahead and down into their slots. From a camera flyer’s perspective, jumpers in the red zone look as if they are lined up in various seats in an imaginary football stadium as them move down to their slots on the field.) A jumper who arrives late in the red zone more than likely has to maneuver around jumpers who are already closing on their slots. He also prevents later divers from getting to their slots. All of this increases the chance of a collision. A more serious situation can occur when a jumper arrives so late that the first wave of jumpers is breaking off. This is not serious if he immediately turns and tracks away with this first wave. If he doesn’t, he risks a head-on collision. Break Off with Your GroupTo maximize horizontal separation and avoid congestion, jumpers on big-ways break off in “waves”. Imagine how congested it would be if everybody on a 100-way turned and tracked at the same time! On a 100-way, for example, the outer wave might break off around 7000 feet, the next wave around 6000 feet, the next wave at 5000 and so on until only the base group is left. Obviously, the outer wave tracks the furthest horizontal distance and the base tracks the shortest. Again, a jumper who doesn’t arrive in the red zone until break off should turn and track with the outer wave. Track with Your GroupWhen their wave breaks off, jumpers should track away in groups. A group can consist of a few jumpers from one whacker and a few from an adjacent whacker with one jumper in the center of the group designated the tracking leader. At breakoff, jumpers from each whacker turn in the direction of the tracking leader, track side by side for a few seconds, then fan out away from the center. A jumper who goes low should move off to the side, assume a slow fall rate, and try to get above the formation until the outer wave breaks off, at which time he should turn and track away with them. Flat Track, Don’t “Dive” TrackA jumper should stay level with other trackers in his group, and everybody should “flat track” to conserve altitude and maximize horizontal separation. “Dive” tracking (very steep tracking) is not acceptable behavior on a big-way,” says Kate Cooper-Jensen, big-way organizer and multiple world record holder, adding, “A jumper can almost stop dive tracking simply by choosing to alter his body position during the turn away from the formation.” To initiate a flat track, a jumper assumes a slow fall position while turning away from the formation, essentially de-arching as he turns. This prevents him from immediately dropping into a dive track below other jumpers in his group. Keeping his hips elevated as he finishes his turn, the jumper then locks his knees, points his toes, and points his head toward the horizon. His arms are initially extended 45 degrees away from his sides and his feet shoulder-width apart. As he picks up speed, he rolls his shoulders forward, and brings his arms closer to his sides and his feet closer together. He should feel the lift as he picks up speed. Open at the Same Altitude as Your GroupAs an additional safety measure, opening altitudes of the various waves are staggered to maximize separation and make it easier for jumpers to account for open canopies around them. According to one theory, groups in the middle wave open at the highest altitudes while the outside and base groups open at the lowest. The result is a curve of open canopies, starting lowest at the base, curving up in the middle then down again on the outsides. ConclusionA successful big-way is a team effort with the goal of building a completed formation the safest way possible. Diving and tracking on a big-way is like driving on the highway. A safe driver knows more than just how to push the accelerator and go fast. He maintains a safe distance from the driver in front, he doesn’t switch lanes without looking, and he doesn’t cut in front of other drivers just to beat them to the exit. He gets to where he needs to be in plenty of time without causing an accident. So does a safe big-way formation skydiver.
-
Many formation skydivers cannot afford a thousand training jumps a year. Some can't jump every weekend. Some are married with children. Some are students. Some live in the cooler climates and can only jump six months out of the year. Yet they dream about jumping on a 4-way team. They try not to get their hopes up though. They figure that only single people or those born with silver spoons in their mouths can afford it. But that way of thinking is changing. More and more, jumpers on shoestring budgets are finding ways to compete on a recreational basis. They are starting to realize that they don't have to spend a lot of money to learn 4-way. Granted, they probably won't compete with Airspeed or the Golden Knights, but they can still challenge themselves and have a lot of fun in the process. So for jumpers who want to jump on a fun team, here are some suggestions for getting started: Do you have the time? Are you willing to commit the necessary time to the team? Things like work, family commitments, and other hobbies have to be taken into account. You might have money to burn, but it won't matter if you're a Boy Scout troop leader most weekends. If you have a spouse or significant other, will they agree to your being gone on weekends? But don't let the term "fun team" fool you. It can actually be more challenging to coordinate schedules for a fun team than for a serious team. With a serious team, members are usually committed to practicing every day of every weekend. With a fun team, however, members must determine which days on which weekends they're going to practice. It takes a little more juggling. Do you have the money? Time and money are the big commitments. Even if you can spare the time, can you spare the dime? Okay, corny rhyme but you get the point. Don't get your teammates' hopes up if you know you won't have the money. Also make sure your spouse or significant other knows how much money will be involved. Can you take criticism? Some jumpers don't like the pressure of competing but perform admirably on recreational jumps. On a team, both your RW and interpersonal skills are constantly under scrutiny. Your every move is going to be caught on video. As coach and friend, Woody (John Woode) always says: "The video doesn't lie." Jumpers who don't like to be under the microscope might want to think twice about signing up for a team. Find jumpers who can agree on common goals Once you decide you have the time, money, and tough skin, look for other jumpers who can agree on common goals for the team. Your personalities can be as different as night and day, but you can still jump together if you agree on common goals for the team. For example, if two team members want to practice full-time, buy team jumpsuits and go to the Nationals, while other members only want to practice two days a month and forget the Nationals, compromise might be difficult to reach. Teams in this situation might want to think about forming two teams, one serious and one just for fun. Ask around and you will find that you have more in common with other jumpers than you think. Most jumpers have jobs, families, and hectic schedules. But that's the beauty of a fun team - it lets you schedule training around everybody's life, not the opposite. Tip: Find a couple alternates who can fill in when regular members can't practice. Set team goals Once you find jumpers with compatible goals, schedule your first meeting. Find a setting for the meeting where everybody can relax and take as much time as they need. Agree to meet as a team at least twice a month. At this first meeting, agree upon basic goals for the team, such as showing up for practice on time and notifying the team if you have to miss a practice. Elect a team captain and somebody to create a team-training schedule. Ask team members to provide a calendar of their availability for the entire season, along with contact information (phone numbers and email addresses). Schedule another meeting to distribute the schedule and clear up any discrepancies. Determine the cost In one of your first meetings, map out a team budget and agree upon how each team member will pay. Let's say you want to make 100 training jumps, attend four meets, and go to the Nationals. Here is an estimate of what it might cost (per person) based on figures from the 2003 jump year in the US. 100 Training Jumps @ $17/jump (including video) $1700 4 Regional 4-Way Meets (6 jumps each @ $21/jump) $504 Team Jumpsuits (optional) $325 Registration for the 4 Regional Meet $100 U.S. Nationals (10 jumps @17/jump) $170 Registration for U.S. Nationals (per person) $60 Transportation and Food $500 Total $3359 Competition is not for the feint-hearted, even when it comes to money. But most DZO's give teams a discount on ticket prices if the team trains at that drop zone and buys tickets in bulk. If each team member purchases just 50 tickets to start the season, the DZO collects $3400 up front (at $17 a ticket). It's money in the bank for the DZO and a commitment to the team from each jumper. Tip: Set a deadline for collecting money for jump tickets from team members. Get good coaching Many DZ's have an RW organizer or coach who is willing to offer advice to new teams. Normally, this kind of advice is free. Even if the coach charges a small fee, it is worth it because it will save you many jumps flailing around by yourselves. Coaching is also available at most local competitions to help teams work out exits and engineer skydives. They can also help with the mental side of skydiving such as how to conduct team meetings and how to mentally prepare for the skydive. So don't be afraid to ask for help. You're only cheating yourselves it you don't. Keep a team notebook In the pressure of training, it is easy to forget what you've learned. This is where a team notebook comes in handy. You don't have to write down everything, just a few reminders about how to do a particular move. Then when you're scrambling to dirt dive at a meet, you can refer to the notebook to refresh your memory. Make a page for each random and each block (currently, there are 16 randoms and 24 blocks in the 4-way dive pool). Tip: Create the notebook on a computer so you can print a copy for each team member. In Summary: There is more than one way to start a team, and the suggestions offered in this article might be old hat to experienced competitors. But for jumpers new to 4-way, they provide a good starting point. If you get nothing else out of this article, remember this. Team jumping is a commitment of time, energy, and money. It is a group effort. Everybody has to be dedicated, committed, and focused. They have to be able to perform under pressure. They have to be able to get along with people. And, most of all, they have to believe in what they're doing. If you are willing to do all this, then what are you waiting for? Go find yourself a team! © January 5, 2004 Edward E. Lightle
-
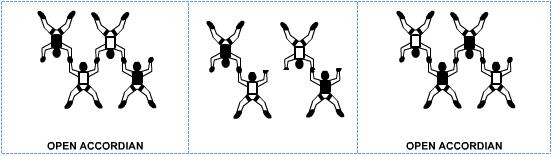
(This article was first published in the August 2004 issue of Parachutist as “One Good Turn Deserves Another”. Since then, the article has been updated and improved.) Turning a piece on a formation skydive is not as simple as yanking it around and hoping it will stop where it is supposed to. Jumpers in the piece must help it stay close and level throughout the turn, and they must help their piece partners start and stop the turn without rotating it too far or slamming it into the other piece. A piece that is yanked around too fast can rotate too far or even injure somebody. A piece that is not completely turned or turned incorrectly can drift away and actually become harder to control. This article shows the correct (and safe) techniques for turning pieces on recreational RW loads. Meet the minimum skill levelBefore jumpers participate in a skydive that involves piece turning, they should meet the requirements for a USPA A license, which means that they can do individual 360-degree turns, dock on another skydiver, maintain eye contact, track, wave off, and pull. In addition, jumpers should be able to dock on small formations such as a 4-way Star. Start with partial turnsNewer jumpers should start with partial turns (180 degrees or less) on small formations. Here is a fun drill. Build a 4-way Open Accordion, break it in the middle, turn the two pieces 180 degrees and re-dock. This puts the jumpers who were on the inside on the outside, and vice versa. In this drill, think more about “trading places” with your piece partner than about turning the piece. The piece will automatically rotate if you move to the slot vacated by your piece partner. As you move, try to help place your piece partner in the spot you just vacated, keeping your piece level with the other piece as you do. Repeat the process to place yourselves back in your original slots then repeat the drill until breakoff. Move on to 360-degree turnsOnce you can do drills like the one described above, you are ready to move on to 360-degree turns on small formations. A good drill for this is the Zig Zag – Marquis 4-way block. A “block” is a two-formation set in which jumpers build the first formation, split into pieces, rotate the pieces then reconnect them to form the second formation. In competition, experienced teams speed up their turns by rotating the end of one piece over the end of the other piece – in essence, reducing a 360-degree turn to 270 degrees or even less. But in this article, we only discuss flat turns because they normally work best on recreational loads where the objective is not speed but smooth level turns. In the Zig Zag – Marquis block shown above: To start the turn, Jumpers A and B break grips and turn approximately 90 degrees to the right and stop, keeping each other in view over their left shoulder (helps them stay close and level). While this is happening, Jumpers C and D stay put except to extend their arms to let Jumpers A and B move. Once Jumpers A and B have moved, Jumpers C and D “trade places”, keeping each other in sight over their left shoulder as they move. When their legs almost touch, they stop, look over the other shoulder (called a “head switch”) and place Jumpers A and B together in the Marquis. While Jumpers C and D are finishing their turns, A and B also do a “head switch” and keep each other in view and on level while they are placed together. All jumpers should help keep the pieces level throughout the turn. Notes: To be safe while they trade places, Jumpers C and D do not move directly at each other, but slightly offset so that their legs do not collide. Also if they focus on “trading places” rather than spinning their partners around, the pieces are more likely to stay close.The same concepts used for the Zig Zag – Marquis example above can be applied to turning pieces in larger formations. Consider the following example. In the 9-way example above: Jumper A turns approximately 90 degrees to the right and stops, keeping the other pieces in view over his left shoulder (helps him stay level and close). Jumper B moves into the space cleared by Jumper A. At the same time, Jumper C moves into the space vacated by Jumper B. As soon as Jumper A feels the piece rotating, he looks over his right shoulder for the other pieces and stays level with them as the turn finishes. As the turn finishes, Jumpers B and C place Jumper A back into his original slot. All jumpers should help keep the pieces level throughout the turn.Note: Everybody’s initial moves should create enough momentum to keep the piece rotating. If it starts rotating too fast, Jumpers B and C can lower their right knee temporarily to put on the brakes. Similarly, if the piece stops rotating too soon, they can lower their left knee until it starts moving again. Rotate pieces on their center pointsTo keep the pieces close throughout the turn, each jumper must help the piece rotate on its center point. Jumpers in each piece should watch the other piece over one shoulder as the turn starts, then “head switch” and watch it come back into view over the other shoulder as the turn completes. This helps keep the pieces close and on level and emphasizes the following point: If you keep your target in sight, you will be more likely to fly to it. Get the right gripsIn the dirt dive, jumpers should practice the grips they will be taking in the air. This way they won’t be fumbling around for grips when the piece starts turning. Also a grip should not hinder a piece partner’s ability to fly. This is especially true of leg grips. Do not grip at or below the knee because this hinders your piece partner’s ability to move his leg. Instead, grip as high as you can on the outside of his thigh so that when he moves his leg your grip doesn’t move much at all. Tip! High, outside leg grips also help people with short arm spans to fly when they have Sidebody grips. Sidebody grips consist of an arm and a leg grip on the side of your piece partner. It is much easier to fly if your arms aren’t all stretched out. Slow is FastIf the pieces drift apart and get on different levels during a turn, jumpers should not try to make up the distance too quickly. They should get the pieces level first then slowly make up the horizontal distance. Slamming the pieces together in a rush can possibly injure somebody or even cause a funnel. At the very least, it creates a wave throughout the formation that must be dealt with before jumpers break for the next point. If jumpers break before the formation settles down, they will more than likely end up on different levels again. It actually takes less time to get the pieces level and fly them smoothly back together than it does to slam them together then have to deal with an unstable formation. As often is the case, slow is fast. Give it timeLike any skydiving technique, learning to turn pieces effectively takes time. Don’t expect to run straight from your A license exam to jumping on the hot RW loads. Practice on small formations first. Do some 4-way; there is no better training tool for learning how to turn pieces. With practice, you’ll learn to anticipate your moves and to work with other jumpers in the piece. Piece turning is definitely a group effort and when everybody is working together, it feels like the piece has eyes and a mind of its own as it does a smooth, quick and controlled 360-degree rotation then stops on a dime and makes a perfect re-dock on the other pieces!
-
You might as well be searching for The Holy Grail. How often have you heard of a team who's had a big argument and broken up before, during or immediately after Nationals, having already spent an exorbitant amount of money? Most of the time this could have been avoided by simple communication, honesty and a little bit of compromise from the outset. Instead, the 'volcano effect' takes hold, and petty grievances, built up over the course of the year, come to an ugly head, usually at an important and stressful event - like Nationals. Quite often the issue that causes the break-up seems pretty minor a couple of months down the line. But it's an all-too-common practice in skydiving, and one that detracts from teams and individuals being able to perform at their best. Most teams require two years minimum to even scratch the surface of their full potential. It takes time for teams to gel to the extent that they have true communication, anticipation and knowledge of working together. But this all-pervasive attitude, which makes it acceptable to break up a team over somewhat insignificant differences, prevents the sport and individual skydivers from growing and progressing. It's the syndrome of seeking the 'perfect' team, and it's become so commonplace in skydiving that we could almost be forgiven for thinking it's acceptable. What is 'the perfect team'Most competitive skydivers have an idea of what the 'perfect' team is. They look at teams like Airspeed, Deland fire and Sinapsi PD, see these teams communicating and performing well, and make the assumption that to some degree, team members are virtual clones of each other. They never see individuals disagreeing or arguing, and believe these must be 'perfect' teams comprised of 'perfect' skydiving individuals with 'perfect' personalities. They imagine how great it would be to be part of a team like this, and that their own problems stem from being unable to replicate this perceived 'perfection' in their own teams.Because of this unrealistic expectation, too many talented skydivers waste their time not training with a team at all. There's nothing worse than not training - in fact, some of my steepest learning curves have come from being part of what could be described as 'dysfunctional' teams. In a similar way, teams waste time by constantly replacing 'flawed' team members in search of the 'perfect' team dynamic; instead they should be working together, getting over personality differences to achieve a common goal, which is performing at the team best. It may come as a shock but - there is no perfect team! The truth is that on any team, individuals have their own ideas, flaws and times of stress - and often disagree with their teammates. Our unique qualities and imperfections make us part of this diverse human race, and differences are inevitable. I can't think of a more diverse group of people than Airspeed 8 - our disagreements ranged from how many jumps to do, to physical training and jumpsuit colours (you should see what we finally came up with in 1996)! Despite this, I often hear how up-and-coming jumpers idealise the top teams and think they always get along perfectly with each other. The result is that when a disagreement naturally occurs on their own team, they assume it's an inherent and insurmountable fault in the team - and subsequently break up or switch members. Differences like this are to be expected, and are part and parcel of team training, no matter what level you're at. A reply I often hear to this is, 'Yeah, but we're not Airspeed,' - implying it's easier to deal with team disagreements and personality conflicts when you're a professional team; if you have to put up with it for 'work', then somehow, you can. But when non-pro teams nowadays are spending between $5,000 and $25,000 per person per year on this sport - it seems like a few minor differences could be worth dealing with for longer than just one season! More to the point - there's really no alternative, if you want to perform, you have to deal! It's easy for teams to think their issues are unique, and that problems can't be resolved because of this; however, the case is most likely that the individuals are not willing to work out their 'unique' issues. Usually the problem is nothing more than the result of someone's need to express themselves, and this, in turn, being taken the wrong way. Problems like this could have been resolved months earlier with the input of a good coach, or by using truthful 'pass the rock' sessions where team members get the opportunity to vent and communicate openly. Teams need to realise that what they're going through is normal, and conflict is part of a natural evolution for every team. There is not a single team that does not go through conflicts. The difference between a successful team and a failing team is that the former works out their differences, whereas the failing team does not. It's not a matter of individuals being unable to resolve their conflicts - it's simply that they are unwilling to. Airspeed has gone through few big decisions without some pretty heated opinions being cast around the room. Because every team goes through the same cycles of development, it's worth outlining what those cycles are, so they know what to expect. One way of looking at how teams grow and mature is to use Bruce Tuckman's 'forming, storming, norming, performing' model. Forming - Stage 1 The 'honeymoon phase'When most teams join up, they all seem to get along - everyone is excited about the new team and keen to get started; this is also known as the 'honeymoon phase'. Most skydivers are jubilant that they actually have a team to skydive with, morale is high, and negative personality traits are kept in check. It's very important in the 'forming' stage to get an experienced coach for guidance and direction. Many teams also benefit from having a team leader, and this is the time to appoint them. You should also spend quite a bit of time discussing your goals and aspirations as honestly as possible, as this will avoid problems down the line. There could be nothing more frustrating than being in a team where people have completely different agendas - one wants to take the team to the World Meet and another just wants to get the swoop at the end of the dive! Levels of commitment in terms of number of jumps, tunnel, money and time should be discussed as a priority, and while not every member of the team will have exactly the same objectives here, as long as they are in the same ballpark the team can succeed. It's important to come to a workable compromise and move on - rejecting a team whose goals don't precisely match yours, and ending up not jumping, is much worse than doing only 200 team jumps that year instead of the 300 you wanted to do! Individual long-term goals can even be different - it's fine if one person eventually wants to become a World Champion, and another just wants to compete for a couple of years before moving on to other things - as long as the collective team goal is agreed upon and compatible for the duration of the agreed term of the team. I refer to this as 'buying into the contract'. The key agreements of this 'contract' are: Individuals agree to work together to achieve the common goal. Individuals agree to communicate honestly with each other, more commonly known as having regular 'pass the rocks'. Individuals value their differences, i.e. they recognise that every person has a different background and personality, and will therefore have different ways of relating and behaving. Individuals seek to gain insider learning about their impact on the team, i.e. thinking before speaking and recognising that what they say has the potential to impact the team in a negative (or positive) way. Individuals should be responsible and accountable for their actions and words. Storming - Stage 2 Guess what? The honeymoon is over!This is the frustrating stage of learning with the team; individual quirks start to come out and team members vie for position as they attempt to establish themselves. Cliques can also start to form within the team - questions and uncertainties come up and the 'contract' itself may be questioned. This is where most teams sow the seeds of inevitable self-destruction. Simply put, this is the stage where arguments might occur over block techniques, individual performance and styles of relating. Even table manners, personal hygiene and fashion sense can all come under attack! It's important to realise that this is natural human behaviour in a goal-orientated team environment. It's also important for individuals and the team to reiterate the goals they set and believe that the team outcome is more important than individual needs. At this stage, outside help in the form of a coach experienced in dealing with team dynamics is invaluable. I've heard more times than I'd like to recollect, 'I guess I'm just not a team-player'. I don't believe this to be true. That individual is just not willing to compromise, or never bought into the 'contract' in the first place. People who are described as 'team players' are just more willing than others to suppress their need to be heard all the time. I also believe there's no such thing as a natural team player. Anyone has the ability to become a team player as long as they are willing, at times, to put aside their own ego for the good of the team. Knowing that the 'storming' stage is normal and can be overcome by focusing and refocusing on the agreed team 'contract' is critical at this time. There's no knowing when the 'storming' will occur, or how long it will last. However the sooner a team recognises it and then accepts it as normal, the sooner the team will leave this phase behind. Norming - Stage 3Congratulations - you've got further than most teams and are on your way to performing your best! This is the phase where the team has recognised individuality as a strength, and has matured as a group. Commitment and unity is strong. It could feel similar to the 'honeymoon phase', but instead of being based on enthusiasm alone, it marks a time of personal growth and acceptance. Roles and responsibilities are clear and welcomed: the team's everyday interactions and dealings have become like clockwork, and the daily training routine, including team meetings and 'pass the rock' sessions, is more instinctive and needs no prompting. It's important to realise the individuals themselves have not fundamentally changed, and disagreements will still occur - however teammates have come to understand that having their personal needs met is secondary to team growth. The same disagreements teams had in the 'storming' stage suddenly seem less important and are dealt with more quickly and in a more mature manner. Performing - Stage 4 The fun part!In this stage the team has a high degree of autonomy and will be running like a well-oiled machine. The team is able to focus on performance; personal issues that would have held them back previously as a distraction have melted into the background and become irrelevant. This is also the phase where individual relationships and trust are consolidated within the group. On a personal level, team members trust that each one will always act for the good of the team - communication between piece-partners is open and honest. In the sky, teams feel that everything falls into an instinctual rhythm, more so than a forced or conscious act. Trust in individuals' ability runs high, allowing team members to be sure that others will also fly their slots with confidence. This in turn allows for faster keys, more confident moves, and ultimately, more points. Teams should expect that disagreements will still occur - even arguments - but now issues are resolved within the team positively. It's also important to recognise that just because a team has reached the 'performing' stage, they may not be the 'best of friends' - however teammates trust and respect each other, because of the understanding that they are all focused on the common goal, i.e. the 'contract'. This phase is more easily attainable than most people think, or believe. It's the most fun part of training, and the pay-offs are numerous. Individual growth, realisation of your potential, a load more points and the best skydiving you'll ever do are just some of them. And it's a choice that anyone can make. Gary Beyer was a member of multiple World and National Champion team, Arizona Airspeed, between 1995 and 2002. He has since retired from World level competition and dedicates his time to team and tunnel coaching. www.onthelineskydiving.com This article was first published in Skydive The Mag (UK) and is republished here on request and with permission from the author. Photos by Mike McGowan
-
Remember when you were a student? Most of us couldn't exit a plane to save our lives (or pass a level), the skydive seemed so short yet so full of things to do, and when it was over we had this nagging feeling of, "If only there was more time!" Welcome to 10-way. If you're an accomplished competition formation skydiver, then 10-way isn't so tough, just another engineering challenge to meet with a little thought and practice. But for most weekend warriors who usually just jump with their buddies to have fun, funneling exits with varying frequency but not quite sure why, 10-way is an event that makes you feel like a student again. But when you start training for 10-way, like when you were a student, a new world of skydiving challenges opens up to you. Not only is it challenging--10-way is also a blast! It's some of the most intense skydiving you'll do, because whatever you do, it's got to be very fast if you're going to be competitive. And you don't have to be a full time skydiver to get good at it. As Roger Nelson, program manager at Skydive Chicago and eight-time 10-way medalist, often said, "10-way is the only discipline at Nationals where you can be a weekend warrior and really compete against the best in the world." For example, Skydive Chicago's STL10 team practiced in the mornings from 7 a.m. to 10 or 11 a.m., stopping to allow jumpmasters and videographers to work for the rest of the day, and still won two gold and two silver medals in four competition years. And who knows how low the time can go? "We're building 9.2-second jumps, thinking we're pretty hot, but Roger's saying, 'I think we can do eights…' and we did," remembers Frank Shisler, member of Skydive Chicago STL10 in 2000 and 2002. "It's all about focus and intensity; once you step in your slot behind that line, it's a totally different world." When you're really training for 10-way, you give that exit and skydive every last bit of effort you've got. To excel in 10-way, that's what it takes. If you just want to play with this new discipline for fun, well, it lends itself to that too. Not being a World Meet event, it tends to be more casual and the experienced teams more supportive than in some other events. This article presents the lessons learned from several years of 10-way experience with a recognized top 10-way team, Skydive Chicago STL10. The concepts explained here are valuable to anyone working on 10-way, and will be most useful for those trying to get past good on their way to great. Your Mission Is…Your goal for every 10-way formation skydive is to build one correct predetermined formation as fast as possible. There's only one point to remember. In theory, it's the simplest competitive skydiving event out there, with the exception of accuracy--get to the right place as fast as you possibly can (or at least faster than the next team). It's almost a drag race between teams, especially in the later rounds. Easy, you say? Not necessarily. To be sure, the "new" rules (which went into effect for the 2002 Nationals and were a screaming success) make things a bit easier than they have been in previous years because they now allow grips out the door. This means that you can launch part or all of the 10-way as a chunk, thus making the exit frame (the position of everyone when the last person exits the door) tighter. Then the early floaters and late divers don't have as far to go to the two unlinked jumpers who form the base, making the completion time shorter. The rules require the first two jumpers in the base to be unlinked, which can happen with a grip flash after launching a chunk. So technically, you could launch all 10 together, let go of the base two, then dock the two four-ways on the base if you could manage it. By the way, all participants except the camera flyer must be lined up behind a line on the floor for exit--no floaters allowed. This line goes from the forward edge of an Otter door to the rear bulkhead on the right side of the plane. Going over this line starts the clock, even if you are obviously just setting up and not ready to exit, so be careful of it until you are ready to exit. You have 35 seconds to build the formation in competition, because a five-second hold time is required within the total working time of 40 seconds. If you take longer than 35 seconds to build the formation, it's a bust and you are awarded the full time of 40 seconds. Why 10-Way?So what exactly will 10-way do for you? It's not a World Meet event. It won't teach you transitions and vertical hops. You can't practice it in the wind tunnel. But it will teach you all about exit dynamics, subterminal relative work, approaching a formation from above or below, and a respect for team cooperation at least equal to that you get from other disciplines. Body position on exit is just the beginning. Since there are no outside floaters in 10-way, the way your body is positioned upon breaking the plane of the door (while driving out the door hard) determines how far you (and anyone behind you) will be from the teammates ahead of you. What you do in that split second determines the outcome of your skydive. Contrary to popular belief, 10-way is not all about diving. The first few people out are dive floaters--they bomb the door, but do so either sideways (with their left sides exiting first) or turning to the right (exiting a Twin Otter) in order to float back up to the base. Between dive floating, setting a base, and diving down to the base, there is a wide range of ideal exit body positions based on the slot in question, and every member of a good team has an understanding of all of them. On to subterminal work. When 4-, 8-, and 16-way competitors say the exit is everything, they generally mean that the exit separates the best from the really good. In 10-way, the exit is almost literally everything. From the instant you cross that line inside the plane to the instant the last grip closes is your build time. Just to give you a little perspective, SDC STL 10 averaged a build time of 9.79 seconds for the required six rounds in the 2002 USPA Nationals (which they won). If we assume that we spend 8 seconds "on the hill" before reaching terminal velocity, and that a fast exit might hit 2 seconds on a really good day, that means that a top 10-way dive is completed before hitting terminal velocity. That's what we mean when we say the exit is everything--building a formation that fast requires an ideal exit and a lot of flying skill on the hill. Once you're out, if you're not the base, you have to dock on it. Since we're talking about sub-terminal hill work, we have to remember that the plane of the formation is still tilted to some degree relative to the ground. Thus, the floaters approach from below and the divers approach from above--which is quite different from the typical larger-formation picture of approaching on level. Here, level is relative to the plane of the formation, not the horizon. And if you want fast times, you don't have time to hit level a distance out from the formation and approach flat. You need the fastest approach, which is a straight line. Besides, if you're building in sub-terminal air, the base is accelerating--so if you pause a ways out, you're usually hosed. Cooperation and consistency among all team members is essential to each member's successful performance and thus that of the team as a whole, perhaps even more so in 10-way than in other competitive disciplines. All it takes is one sidestep by one person early in the lineup to hose the whole skydive by giving everyone else an exit they didn't expect (perhaps even involving the infamous door strikes). In a 35- or 50-second skydive, a bump on exit is much smaller in the grand scheme of things. But if your build time goal is less than one-third the working time of a 4-way jump, every fraction of a second counts. That's why every member of a 10-way team has to be on the same word, not just the same page, in order to succeed. "You change one person, you change the whole thing," says Shisler. "If you want to be competitive, you have to put in the practice with the same people in the same slots." Also, the cohesiveness and discipline you learn with 10-way will benefit you in any other competitive disciplines you choose. You get all of these benefits from doing competitive 10-way, and you get to have fun too! The fun and bonding between team members are the biggest reasons why several teams, like SDC STL, compete together with minimal lineup changes year after year. Exit ChallengesDiving out of a plane solo isn't so tough, but if you want to be in the same time zone as your teammates when you exit for 10-way, some grips are quite helpful. So now you're diving out some number of people as a chunk. That doesn't mean that you have to hold onto them forever--the people just behind the base and the divers behind them generally find that holding on just long enough to ensure proximity through the "snap" on exit is all they need (floaters tend to do best without grips, as dive floating individually is enough work). Thus, if you are one of the jumpers with a grip on exit, your hold time and release timing will be engineered through trial and error, and consistency is an absolute requirement. Letting go of only one hand earlier than usual will spin the person you're holding. Letting go of both hands early will leave you and everyone behind you too far away (or the floaters too far away, if you are early in the lineup). Letting go too late might screw up the person you're holding. Setting up behind the line is a lot like The Price is Right--you want to be as close as possible without going over. As stated earlier, this starts the clock whether the offending body part is a foot over the line or a head leaning over it. Think of the line as a plane, not just a line on the floor. Your exit setup will go through a lot of changes before it settles into one that is good for everyone. Practicing on the ground with rigs is a helpful start, but the actual skydives are the real test. Once you've settled on an effective lineup (Jane's foot here, Bill's knee tucked in just so), stick to it unless you're trying to improve something and you let your teammates know. As previously stated, your exit affects everyone else's--so if you're going to change something, talk about it. Movement on exit is another challenge--not everyone can move at the same time. If you're first out and start the clock, be sure that you go at the same point in the count, not leading the GO! one time and going right on it the next. This helps set the timing for the later divers, who have to be leaning in the right direction at the right time to exit with the team without either running people over or getting caught napping and being dragged out the door. "You're skydiving from the word 'HOT!' " says Shisler. "A lot of casual teams get out (of the plane), get stable, then get together. You can't do competitive 10-way that way. You have to be flying together from the word HOT! A lot of people don't understand that." Also, using the door side of the plane for balance is not allowed under the rules, whether during setup or on exit, though you can use the opposite side. (Note: if you lean on that side of the plane, be sure that no part of your rig is caught on a bench or seat belt bolt. I can tell you from experience that this definitely hampers your exit…) Your balance, which is essential to a good exit, depends on your agility, your teammates' balance, and a smooth jump run. Speaking of jump runs, consistent airspeed as well as a smooth flight is essential. When traveling to different drop zones, or even with different pilots at home, we found that changes in airspeed produced noticeable changes in the exit frame. With higher airspeeds, everyone is more separated and the times are longer. With a slower airspeed, everyone notices a steeper exit frame and often a longer build time because of the different angle, despite being closer together. So, basing practice flights on the airspeeds specified in the competition manual (85-95 knots) is a big help to a seriously training team. If jumprun is bumpy, your exit will stink. It's guaranteed. Don't be afraid to call a breakdown of the lineup and a go-around if the floor is rocking and rolling, especially in competition. Formation Build ChallengesSo now that you're out the door, for most of you it's time to chase the base. You might be tracking uphill with everything you've got, or diving and hoping you can stop without sacrificing a teammate. Either way, aiming for a target when both you and it are on the hill can be tough. If you are building a 10-way quickly, in subterminal air, it's a big game of acceleration control--not position control. If you're the base, you try to keep acceleration constant. If you're a floater, you are trying to slow your acceleration and then match the acceleration of the base. If you're a diver, you're accelerating more and then trying to slow--not stop--your acceleration to match that of the base. Matching position with a stationary target isn't so bad, but the acceleration game is a challenge. Add to that the fact that you are working in "mushy" subterminal air, and the degree of difficulty rises again. It's a lot harder to make these acceleration changes at this time than it would be in terminal freefall, especially right out the door. Respect the fact that things just don't work quite as well as you want if you're not used to a lot of subterminal maneuvering, and take it easy the first several times. Hitting the base hard can take it out, or it might just change its angle enough to make it cut into or surf on the relative wind more than it was doing before you hit it. This will change the base's position from its normal exit frame, hosing the floaters and divers who haven't docked yet. With a highly practiced team, everyone gets accustomed to a certain exit frame after a certain amount of practice and is already going to that familiar spot on exit rather than waiting to see what the base does. When that spot changes, it messes up things for everyone. Of course, at some point everyone has to cross the line in order to figure out just where it is…the takeouts can be spectacular. Your vertical approach isn't the only thing that requires a lot of care--you don't want to hit the formation hard on the horizontal plane either. It's essential that the angle of the formation remain the same, ideally where it was planned to be. Large changes in the angle during the build screw up the approaches of everyone who isn't yet docked. When you're approaching the formation on the ragged edge of too fast to stop, it's pretty tough to adjust to an angle change. Then, although it's best not to throw off the angle in the first place, it's not necessarily good to quickly fix it either. When time is short and the angle is off, those still approaching are already adjusting their approaches to compensate for the problem. If the base puts the angle back where it was, then those still approaching could be going the wrong way--to the temporary "bad" angle they saw just a second ago. Figuring out how much angle change your team can handle takes a lot of practice and awareness in the base and late floaters/early divers. Last, but certainly not least, of the formation build challenges is that of grips. It's easy to snag the first bit of the right arm or leg that comes near you, but it's absolutely vital that you get a solid grip the first time, not just grabbing a fold of a jumpsuit and hoping it will hold. There can be a lot of tension in a fast 10-way build, and you'll surely get a lot of grief if you're the one who lets go. Another thing about grips--if you are on the front of the triple diamond, you have no grips. However, if you keep your hands out wide and overlap the hands of the person next to you, it can look like you do--this will look like an incorrect formation. As in the smaller-way RW disciplines, you have to present the formation to the judges correctly in order to get scored. Each slot carries the responsibility for this. Slot SpecificsFirst of all, the exit is roughly a single file line. Many teams will stack the first couple of people out the door or curve the lineup to shorten its overall length from the door, but the later divers tend to do best when exiting single file so they don't interfere with each other during side-by-side exits. The early slots (usually 1-3 or 4) are the floaters, the middle slots (usually 4 or 5-6) are the base, and the last to exit (usually 7-10) are the divers. Floaters--For decades, late divers have had the "glory slots" on larger formations because all eyes were on them as the formation completed. In 10-way, the ideal situation is for the last floater and the last diver to dock at the same time, so there's a lot of healthy competition between the two groups. "If you don't get out of the plane in a mode that propels you up, then you're behind the curve and the divers beat you every time," says Ron Olson, four-time 10-way medalist in slots 1 and 2. "You've got to know where your target is--the sooner you spot it and the angle it's coming at you, the quicker you can adjust to where you need to go. You need to be able to cup air and look where you're going at the same time, and go where you look. You're pointing your toes and driving at it hard, then all of a sudden you're level with it, it's coming at you, and you're trying like crazy to stop. "The rest of it is looking at the divers and knowing that if you slack off, they'll beat you there," he laughs. With a quick build, floaters certainly have to work hard. First they're anchoring in the airplane to stay behind the line even though others might be leaning on them, then they're going up as hard as they can go, then they're stopping as hard as they can and punching out a hard arch to stay with the base as it continues to accelerate. No 10-way slot is for tentative flyers, but the floater slots in particular are best filled by skydivers who know how to get maximum performance out of their bodies--whether it's tracking up hard, slamming on the brakes with your knees almost in your chest, or backsliding in your slot to keep up with the formation sliding down the hill. And like divers who need to go fast and stop quickly, floaters benefit from a lighter body type. "Lighter people have a better chance of recovering when they're behind the curve," Olson notes. However, you have to be able to match the base's fall rate when you dock, so if you are so light that you can get to the formation quickly but not stay down with it, you might need weights even if you are a floater. Another key to a good floater performance is a consistent base, says Paul Wold, four-time 10-way medalist in slots 2 and 3. "You've got to leave the plane going to your slot on the base, or you're too slow. But you can't leave the plane going to a spot like that unless the base is in the same place every time." Base--Just in case you haven't heard the word "consistent" enough yet, "consistent" is the hallmark of jumpers suited for these two slots. The 10-way is "initiated by two unlinked jumpers"--that's you. Your job is to get out of the plane the same way and speed every time, and to set a stable fall rate every time and a stable heading for each formation. It sounds like a job for a drop-test dummy, but it isn't. On exit, you might have two or three people hanging on you, so not only are you towing them out as you start the "train," you also get to deal with any of their issues as well as your own. It's your job to fix any problems that arise so that you exit where and as fast as you are supposed to be. Regarding the formation build, as anyone who's done larger formations will tell you, sometimes you have to fight like hell just to stay still when other people are docking on you. And of course, all the effort you put into staying still includes vertical and horizontal force, and it's tougher to fly hard in mushy sub terminal air. Base flyers should ideally be skydivers with lots of subterminal maneuvering under their belts, not career-long late divers or super floaters. People who are used to a lot of contact and working towards multiple points (particularly with competition RW teams) tend to have the subterminal flying skill and solidity (sometimes described as "roots in the sky") that these slots really need. Solidity means that when someone docks too hard, you can almost instantly adjust to minimize their effects on the rest of the formation. This requires split-second reactions and strong flying skill, the kind an instructor needs when manhandling a creative student. This slot isn't for "delicate" flyers who are easily bumped out of position. Also, the base can't be maxed out in terms of fall rate (slow or fast), because the adjustments could go either way (more on weights later). Position isn't just related to fall rate and your spot in the sky, it also involves the right angle for everyone. You'll find that once you get your exit to be fairly consistent, everyone ends up in about the same place relative to each other in the exit frame. So you plan each formation's angle to give everyone the shortest approach to their slots. If the base doesn't set that ideal angle, then everyone has further to go and thus the time is slower. And as previously discussed, maintaining the angles throughout the build is also the job of the base and anyone who has already docked. With practice, you develop an image of the exit frame you expect to see, and any significant changes then offer the option of accommodating them. If, for example, a floater flipped on exit and dropped down, you might punch it out a bit to help them out. But you don't want to go all the way to where they ended up, because then you make nine people work to save one. Ideally, you go to a point in between where everyone else goes a little further, and that floater goes a little further, and your time is better than if you went all the way to the floater and made the divers make up the entire distance. Divers--Even experienced large-formation divers often get humbled when they switch to a good 10-way team, because much is the same, yet much is different. If you're building a fast 10-way, the divers can't go into a max no-lift dive at all because they'll blow right past the formation (this is the most common mistake). As stated earlier, this is a game of acceleration control, with emphasis on the control. It starts with "not listening to the count, but feeling movement and being prepared," says TJ Hine, two-time silver and two-time gold medalist in 10-way with Skydive Chicago STL (TJ has been #9 for the last two years). "You've got to be skydiving from the word 'HOT!' " The right exit for a diver is one where he isn't getting pushed or pulled, instead flowing out the door smoothly behind his teammates with grips on the laterals to maintain proximity out the door. Hitting the door is a concern for the later divers, but tends to start earlier in the lineup (such as when someone in the middle or an early diver cuts the corner to the right when exiting). Thus, the divers mainly rely on their teammates to put the train in the middle of the door so that everyone makes it out clean. Shin guards on the front of the shin or the outside of the calf can be quite helpful when working out lineups and exits early in the season. Once you're out the door, "The big thing is how you release--you can push people around with the release, but don't hose your teammate," says TJ. "Figure out where the air throws you with your release and don't fight it. Design the formation from there, not from the lineup." For example, Skydive Chicago STL designed formations so that #9 was the last one in, not #10, because #10 (Tommy Shannon) always got thrown past TJ and to his right on the release, in a leapfrog type of move. Next is the approach to the base. "The big thing is being aware of the base as fast as possible, not so much the person you're docking on," TJ explains. "Go for your airspace relative to the base." If you chase the person you dock on, then if they are out of place, so are you. When slowing down to dock, you might find that swoop cords or baggier suits are quite helpful to a diver. As with floaters, leaner-bodied jumpers have a better time with diver slots; the floaters need to conserve altitude early, while the divers need to do so at the end of the approach to keep from passing the base. Also, as with all slots, you have to hang on tight when you get there. "You need death grips on first grip," TJ adds. "The later guys can really put tension on the formation. "The faster times are when people don't think, just react," he summarizes. Weights and SwoopsIt's well recognized in smaller-way RW disciplines that weights are necessary to equalize fall rates for various team members, and 10-way is no different. Whatever it takes to get all members to a matched mid-range fall rate, whether it's weights for one or a looser suit for another, then that's what should be done. For example, as stated earlier, if you're a floater with a small build relative to your teammates, you might still need to wear weights in order to keep up when docking on and flying with the formation. The base might experiment with weights for a time, especially if all floaters or the divers are consistently faster to the base than the opposite group. Weights seem to have a significant effect on the base's initial acceleration out the door, which is what the floaters and divers evaluate for their target position. As previously stated, the fastest times are when the last floaters and divers dock at about the same time, so if one side has an advantage, you have to "handicap" them to get a better overall time. As a diver, however, you probably don't want to wear weights unless absolutely necessary to match the formation's fall rate, as they decrease your ability to slow down your dive. Regarding slowing the fall rate, remember that major changes in fall rate are the norm for non-base flyers in 10-way. Swoop cords are often used by divers to make the change from fast to slow easier, smoothing their docks. Swoops can be very handy for a diver who needs to stop hard, but make sure that they're not so tight that they restrict your movement. It's not good if they float you up in the formation or keep you from reaching your toggles comfortably. VideoLast but certainly not least of the slots is your (hopefully) dedicated videographer. As SDC STL's 2000-2002 videographer and proprietor of Skycam Productions, Mike Wood, says, "If it's not on video, it never happened." What's the most important thing about capturing a fast 10-way on film? "Don't screw up," Mike laughs. "I carried two cameras in competition just in case. There's absolutely no room for error. If a floater or diver goes low, they can fly back up and maybe get a worse score, but not having video gives you a 40 (the maximum score). You have to be there absolutely as quick as possible. If I'm one second behind, it costs the team. You have to be there before the last floaters and divers so you can see the last grip close on video to stop the clock. "A lot of people don't take filming 10-way as serious as other disciplines because it's fun," he adds. "But it can be a very competitive thing just like 4-, 8-, and 16-way. It has its own challenges that make that one point very difficult to do fast, as well as filming that one point. With unpracticed teams, it might be 10 seconds before the first two people hook up. With us, it's over by then. There's no time to screw up and fix it. We're shaving tenths of seconds, not 5-10 seconds per jump. Even a 12-second jump is over very fast. "To me, the biggest challenge is getting in your own little spot in the sky without hitting the floaters or the divers," Mike continues. "The exit is coming out so fast (with a medal-class 10-way) that you have to jump many times with the same people in order to learn to react to the base's colors. You have to let half the lineup go past you to (be in position to) film the break in the base grips. Then you have to beat the floaters and get up over the top without running into the divers, because now you're close enough to get in their way if you're not careful." So what's the procedure for getting the perfect 10-way video? Mike is happy to explain. First, you have to be solid and ready to hang on for awhile on climbout, he says, to allow the team to set up inside. "I usually hook my left foot inside to help hold on, then pull it back when the last guy steps into the lineup," he says. "It helps signal the front guys that the count is coming, too. And you have to know how to angle your head to see the whole line before exit. You want it clearly shown, not on the edge of the frame. But don't put your head in too far--one fill-in videographer learned that lesson when he got his lens peeled off by the first guy out the door. "Then on the count, you watch the blur of bodies stream past until the base colors come out," he goes on. "A lot of times, you drop off a little too soon until you get used to your team. I'd slide down the fuselage, not out to the side, since as the floaters hit the door they are immediately spinning around to come back up and it's easy to get in their way. Then you pop up to stay out of the divers' way. You have to get right over the top; if you're too flat, you can't see all the grips. "It's not hard so much as practicing with your team a lot to learn where to be and where not to be," he sums up. Training Logistical ChallengesWith all the jump mechanics out of the way, you might wonder what could be next? The answer is: Lots! For example, if your team can build a 10-way in under 15 seconds, why go to 13,000 feet? You can do training jumps from a lower altitude, saving time and money, and allowing easy back-to-back loads if the rest of the load is climbing to full altitude. For the last three years, Skydive Chicago STL ended up doing training jumps from 6,000 feet--sometimes as low as 5,200 feet--and still built the planned formation nearly every time. However, keep in mind that if you only allow enough altitude for a fast build time, you can't rebuild a funnel--so don't try. A good bet is to plan enough altitude to accommodate your fastest build time plus at least ten seconds to allow a build in spite of a bobble. Besides, you're supposed to hold it for 5 seconds anyway--it's good to get in that habit early. Another key is to document your progress--write down your build times on the various formations every time. That way you can see which ones you need to work on, and which ones you can't wait to draw at Nationals. Thirdly, we've all heard the old saw about how you play like you practice. Well, that means you have to practice like you'll play, which means practicing all or most of your jumps out of a Twin Otter, as that is the only aircraft used for 10-way at Nationals. Not only do you require a Twin Otter, you also require a Twin Otter flying at the same airspeed (85-95 knots) as are specified in the USPA Skydiver's Competition Manual. It's a good idea to check with drop zones where Nationals have been hosted to see what exact airspeed and power settings have been used in previous meets to ensure consistency between practice and competition. The last significant training hurdle is that of over-analyzing the skydives. We all know that each skydive is a little different (or a lot!), but that's easy to forget when you're looking at only 10-second skydives and working towards cookie-cutter consistency. Don't get too bogged down in the particulars of every single skydive--look at your team's performance over a period of time and jumps before you make conclusions about your improvement or backsliding. There is certainly a lot of effort, thought, and engineering behind a successful 10-way team. But there is also a lot of camaraderie, friendship, and learning--there has to be for 11 people to keep working towards the common goal of a highly competitive 10-way. Not to mention the pure thrill of achieving a fast time with the simultaneous cooperation and skill of 10 of your closest friends. The challenges of navigating the road to top-level competition status, both technical and cooperative, make 10-way competitors better all-around skydivers--who had a blast while they were getting better!
-
With today's fast fall rates, weights are essential for lighter weight jumpers. Small jumpsuits are not enough, especially when jumpers in the base are also wearing smaller jumpsuits. There is nothing more embarrassing than making a nice swoop to your slot only to pop three feet above everybody else when you break for the second point. Been there, done that. But it is not as simple as just slapping on ten pounds of weight and swooping. There is a learning curve involved. Jumpers wearing weights for the first time face the fear of going low. They have to learn how to fly with the extra ballast. They have to learn how to fly like a heavier jumper. That means they have to set up a little higher on approach. They also have to stop a little sooner then they are used to doing. Maybe for the first time, they have to fly cautiously. And some jumpers have to learn how to use different amounts of weight for different sizes of formations. It is a challenge, but one you have to face head on if you want to get invited on the good loads. For jumpers wearing weights for the first time, the roles can suddenly be reversed. The big boys in the base might get their chance to watch the lightweights sucking air as they go low. (I'm sure this puts a little smile on the big fellas' faces.) But don't fret. Show the big boys how quickly you can pop back up and get in. For those of you who have never had to worry about going low, here's a little primer. If you go low, move away from the formation and turn sideways to the formation. While keeping the formation in sight, lower your head and spread your arms and legs out as far as possible to assume a flat stance. Push down on the air as much as you can with your hands and feet. Crunch your gut muscles if you have to. Hold this position until you are far enough above the formation to make a good approach. (Forget the old 'hugging the beachball' theory. That actually lets air spill out all around you.) Let's say you made it in and you're fairly proud of yourself. You glided smoothly into your slot without having to fight to stay down with the formation. Of course, you had to watch your altitude. No more approaches from below the formation. The weights kept you honest. Now it's time to move to the next point. When you let go, you feel like you're in sequential heaven! You don't have to swim and flail to stay down with the big boys. You simply move laterally to your next position. What a treat! But don't get too cocky just yet. The next point is a "floaty" one. The big boys in the middle quickly build a 4-way compressed accordion and you are moving around to pod the end. "What happened?" you think as you sink two feet below your slot. Whoops! You've never had to watch your altitude this closely before. "Hee-hee!" go the big boys again as they watch you recover (again). But you're a good jumper and it only takes you a second to pop up and move into your slot. You tell yourself that you'll watch your altitude a little closer on the next move, and you do. The last point is a round and you feel like one of the big boys as you meet them in the center and don't have to work to stay down with them. "Piece of cake," you think to yourself. As you track off, you feel some of the old cockiness returning. But the cockiness starts to fade after you land and start wondering if the big boys will let you jump on the next load with them. Well, don't worry about it. You might not be ready for another big-way just yet. In fact, your next step should be to check out the weights on some smaller formations, preferably 4-ways. Remember I said that some jumpers have to use different amounts of weight for different size formations? So don't rush things. Check out the weights on several smaller ways. Depending on how often you make it out to the DZ, this could take several weeks, even months. Just remember that you are learning to fly all over again. You might have gotten into some bad habits by flying like a lightweight. I know I did. I had gotten used to diving down and not stopping until I was level with the formation. Then I'd make a perfectly level approach from where I had stopped. Boy! Did I ever get my wake up call the first time I tried this with weights. Another factor to consider is where to wear the weights on your body. From my experience, vests seem to work better for women and belts for men. It's just pure physiognomy. Women are typically lighter in the upper torso area, men in the hip area. But this isn't a hard and fast rule. Take me for instance. I wear both a vest AND a belt, but I only carry three pounds in the vest, whereas I carry six in the belt, nine pounds in all. What works for one person may not work for another. A couple of guys at my home DZ wear about ten pounds in a belt. All I know is that without the weights I wouldn't be jumping on the hot loads at my DZ. I wouldn't be doing hot 4-way either. I'm sure if you talked to my DZ's head organizer, he would tell you that I have made great strides in my performance since getting the weight thing figured out. It was hard work but it was darned well worth it. I know I'll be in some of the hot skydives in the year-end videos!
-
I've seen a lot of skydivers who want to improve their sequential skills but don't quite know how to go about it. They jump their butts off but never seem to get any better. They learn just enough to dive down and latch onto somebody, but that's about it. Somehow, they fell through the cracks when it came to learning the basics. I blame some of this on experienced skydivers who don't take the time to work with up-and-coming skydivers. I blame some of it on the speed with which we whisk jumpers through our training courses. I blame some of it on the instructors for not making sure students can perform basic freefall maneuvers. And I blame some of the students, themselves, for not asking for help. So, for those of you who may have fallen through the cracks or want to improve your flying, here are a few simple ways to tune up your freefall skills. Learn to Calm DownYou can't enjoy or concentrate on a skydive unless you are calm. There is no magic formula for achieving calmness -- it is just something you have to do on your own. Exercise, proper rest and diet can help, but inner calmness is something you have to find within yourself. Just try to leave your troubles behind when you come to the drop zone. Focus on enjoying your day of freedom. Breathe -- take slow deep breaths both in the airplane and in freefall. Stay mentally focused but relaxed, not tense. Learn to filter out distractions right before and during the skydive. There are a lot of distractions on a skydive (people talking in the aircraft, the sound of the engines, the wind, your fear of forgetting a point, and yes, even your fear of falling). With practice, you can learn to filter out distractions. Think about your skydive and how good it will feel once you're in the air. Establish a Good Fall RateBefore you can do anything related to sequential, you must fall at just about the same speed as the other jumpers. Before you find yourself floating on a big-way sequential dive, check your fall rate on a smaller one. Do a simple 4-way maneuver (star to open accordion and back to a star, for example). Monitor who is falling faster or slower. Try to find a common fall rate for your group. Heavier people, or faster fallers, should wear a jumpsuit with a little extra fabric to slow down their fall rate, and slow fallers should wear tight suits and weights. Finding this common ground is sometimes easier said than done, especially if you are jumping with different groups. But try to work out the fall rate first before moving on to more advanced moves. Start Small and Get CoachedPractice 2-, 3- and 4-ways instead of trying to get on the big-ways right off the bat. If you're a student or just getting into formation skydiving, this is what you should be doing anyway. If you have been jumping for some time but are still having problems, you might have to swallow a little pride and go back to the basics. In either case, get an experienced skydiver to coach you and your group. Don't waste time floundering around by yourselves. Get your jumps on video if at all possible. Make each jump count. Practice! Practice! Practice!Try to make several jumps with the same group, and make as many jumps as you can back-to-back. Even if you can't afford to jump every weekend, lump several jumps together when you can jump. Skydiving is no different than any other sport -- you have to practice to be good. Give Yourself Time to LearnDon't expect to fly like a pro in one or two weekends. If that were possible, you wouldn't see 4- and 8-way teams making 10 jumps a day every weekend all summer long. Tell your friends you're taking some time away from big-ways to work on smaller formations. Don't worry, they won't make fun of you. They'll probably respect you for trying to improve your flying skills. They might even be a little envious that you're doing something they might need but are too proud to try. Better yet, some of them might join you. Skydive in Your HeadWhen you can't practice for real, go through skydives in your head. I do this a lot, and for good reason. I live in Ohio where it's tough to jump during the winter. So I do a lot of mental skydiving. I go over 4-way block sequences. I design skydives, then go through them in my mind. After a day of real jumping, I always review the day's jumps during the drive home. It's the same thing football and basketball teams do after a game -- they review the game film. Speaking of videos, they are wonderful training tools, but they cannot substitute for instant replay in your head. Which brings up another point -- always get a debrief after the jump. A good coach or organizer always does this. It helps you remember the skydive better, especially the parts that need work. Enjoy the Skydive!Last but not least, enjoy the skydive from exit to landing. Feel the formation leave the plane as one coordinated unit. Ride the exit and smile as you look for the first key. Then feel yourself glide, relaxed and controlled, to the next point. Keep that smile and relaxed control as you go from point to point. At breakoff, contain your enthusiasm until you clear and pull. Then hoot and holler if you want. It's your skydive!