Airport Safety
Never smoke around aircraft, hangers or pumps. Both aviation fuel and aircraft dope present a great fire risk.
When moving light aircraft, be careful where you push. They are covered with very light fabric or metal and are easy to damage. The pilot will show you where it is safe to apply pressure.
Beware of the prop. It is difficult to see and will make quick mincemeat of anyone who walks into it. Always walk around the back of fixed-wing aircraft and in front of helicopters. Stand where the taxiing pilot can see you; his or her forward visibility is not good. Get into the habit.
Leave the dog and the children at home, the airport is not a nursery. If a play area is made available to children at the DZ, remember that they are still your responsibility.
If your airport has more than one runway, stay off the active one. It will normally be the one running the closest to the direction of the wind. Remember that planes usually takeoff and land into the wind so look for them downwind. Rules change from airport to airport and at some you will not even be allowed to cross the active. Do not walk down any runway and do not fly your canopy over one under 500 feet.
Be nice to all the pilots, they have a lot of clout at the airport and you may need one to fly the jump ship. Be patient with the whuffos (spectators), they are public opinion.
Skydiving Incident Reporting: For Mass Media Reporters
Reporting a skydiving (or any other technical sport) accident isn't an easy job, but making the effort to do it thoroughly can give your readers a better product that tops competing publications in this area. Why is improving coverage of this relatively rare event important? The reason is because turning out boilerplate or inaccurate coverage of these incidents angers many skydivers, who might then become ex-readers, and gives the non-jumping segment of your audience nothing special to take away from the story and thus doesn't reinforce your publication's brand.
Accuracy, Not Generalities
Before you think I'm suggesting that you write a full investigative report of any sport accident, let me say that I don't suggest any additional words in your reports. What I am suggesting is making those words count, with more solid information. Often the sentences that appear in skydiving accident coverage are misleading as to the true nature of the accident. For example, the explanation of "The parachute failed to open" that is so often used in such reports is not a simplification for an audience uneducated about skydiving; it's just plain wrong nearly all the time. It's comparable to saying of a single-vehicle accident, "The car failed to stay on the road," implying that the car is at fault rather than the driver.
Such a statement implies that the skydiver did everything in his power, correctly, and still his/her equipment failed to function. However, this is exceedingly rare-occurring far less often than once per year. What is far more common is that a skydiver makes a mistake landing a perfectly good canopy (39% of the 35 U.S. skydiving deaths in 2002, the most common cause of death), collides with another skydiver in freefall or under his parachute (21% of the 2002 deaths), or fails to respond correctly to a survivable equipment malfunction (12% of the 2002 deaths). (Note: skydivers do carry reserve, or backup, parachutes; a malfunction of the main parachute does not automatically kill the skydiver.)
We all like to think that we'll make all the right decisions when the chips are down, but the unfortunate truth is that nearly all skydiving deaths are caused by "pilot error"-a mistake on the part of the skydiver. This doesn't mean that we have to crucify this person who made the mistake, but we shouldn't imply that the equipment was at fault when it wasn't necessarily the main factor in the accident.
Getting the Scoop
Reporting the specific cause of sport accidents gives more "meat" to your story, which both your skydiving and non-skydiving readers will appreciate. But how do you know what to write when you're not a skydiver and don't understand the topic you're supposed to report? Work with the experts-foremost of whom is that drop zone's safety and training adviser (S&TA). The S&TA is an individual appointed at almost every drop zone in the U.S., and abroad, by each Regional Director of the United States Parachute Association (USPA), regardless of whether or not the drop zone is a Group Member of USPA. This individual is tasked with many different safety and administrative-related duties at their appointed drop zone, one of which is investigating skydiving accidents and fatalities. Investigating incidents is one of the less enjoyable responsibilities of an S&TA.
Other interview possibilities include the coroner (if the skydiver involved is deceased) and the rigger (person licensed by the Federal Aviation Administration to pack reserve parachutes, and usually knowledgeable about skydiving gear malfunctions) who inspected the gear--if applicable and if the S&TA directs you to talk to this person. A third possibility is the drop zone owner/manager if an S&TA is not available. The USPA is a good source of general skydiving information, but is not a good source of information on specific incidents.
The local sheriff or a representative often becomes a media liaison by default, but unless this person is a skydiver working closely with the drop zone's S&TA, then working only with this person is not good. A sheriff with no skydiving experience is no better information source on a skydiving incident than a reporter with no skydiving experience, and will often garble information he or she is given simply through unfamiliarity with the topic.
Ask the previously listed skydiving professionals to explain to you, in layman's terms, the cause of the accident so that you can accurately report it. They may not yet have all the answers, especially if certain equipment malfunctions are suspected, but if you are polite and interested rather than forceful about getting the story before an early deadline you will get a lot more cooperation. A good working relationship with the drop zone in question is ideal, because not only will this help you on this story, but you will also get a much better story for other drop zone events such as charity fundraisers (skydiving is interesting to your non-skydiving readers, and can sell publications when good events happen as well as accidents).
Introducing more specifics to your report will be good for your readers, but more information requires more fact-checking. If possible, send a copy of the article to your source at the drop zone before publication. The source will likely jump (pardon the pun) at the chance to review the coverage for accuracy.
Don't Make These Mistakes
Skydivers do not skydive because of a death wish. If that were the case, they'd only make one jump apiece. They most definitely are thrill seekers, but they are dedicated to skydiving safely, even while pushing the envelope, so they can continue to skydive. Portraying skydivers and skydiving as irresponsible, imminently dangerous, or suicidal is an inaccurate disservice.
It is also inaccurate to imply that drop zone management is to blame for most skydiving deaths, because it is every skydivers' choice to exit the aircraft; once they have done so, the only person who can keep one safe is himself/herself. For the most part, blaming a drop zone for an experienced skydiver's death (nearly always skydiver error, as previously stated) is similar to blaming the highway system for a motorist's death. The system simply provides the place for the motorist to drive; the drop zone merely provides an aircraft and landing area for the skydiver to jump and land. What a skydiver does with those resources is his or her responsibility alone.
Also, keep in mind that stating or implying that a drop zone is to blame for an incident could lead to a libel suit if there is no evidence to back up the accusation.
While the following isn't technically a mistake, it is the author's firm belief that in most cases, the practice of including a roll call of any deaths that have previously occurred at a drop zone (or any other sports facility) with an accident article serves no good purpose. If all of these deaths were attributable to the management or equipment provided by the drop zone, then there is something going on that should be exposed. Without proof of such culpability, however, listing previous deaths generally just angers skydivers and creates the mistaken assumption by non-skydiving readers that there is something going on that should be stopped. Again, keep libel laws in mind.
Jump Plane Accidents
Thankfully even less common than skydiving fatalities, jump plane accidents present a different reporting challenge mainly because aviation accident investigation falls under the authority of the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB). The local skydivers might or might not have an aviation and accident investigation background, and might or might not know the cause of the accident; they are not the people you should interview about aircraft incidents. Just because the accident involved a jump plane doesn't make it a skydiving accident. The pilot would be a good source if he survived, but NTSB is the final authority on aircraft accidents, and their reports tend to take some time to come out. They do send public affairs officers to the scene of aircraft accidents; these people are the ones you should talk to in this instance. Resources for journalists regarding aviation accidents can be found on their web site at www.ntsb.gov/events/journalist/default.htm.
The end goal of this article is more informative, balanced, tasteful reporting of skydiving and other sport incidents in order to better serve readers and thereby the commercial publications they purchase.
Thanks to Randy Connell, S&TA, S/L Instructor, AFF Instructor; Chris Schindler, ATP, CFII; and Jim Crouch, AFF/I, USPA Director of Safety and Training, for their contributions to this article.
Resources:
www.uspa.org
www.ntsb.gov
Christy West is a journalist and gold/silver skydiving medalist with over 1,800 jumps.
Skydiving Incident Reporting: For Skydivers
None of us want to think about a member of our skydiving family getting hurt or killed, much less getting hurt or killed while skydiving. Even further down the list is having to talk to a journalist about a skydiving incident. As distasteful as it is to try to explain to a whuffo reporter why a fellow skydiver was injured or killed while jumping, though, it's actually an opportunity to improve the image of the sport.
As we well know, most journalists aren't skydivers and at best have a tough time explaining the circumstances of a skydiving incident. They often get it wrong with a common theme of "The parachute didn't open." But while it is certainly their responsibility to get the story right, they can't do it without help from the experts-which in this case is you, the skydivers who were present during an incident and are designated media contacts.
Avoidance and condemning of the media for their often poor explanation of skydiving incidents is common among skydivers, but we can do the sport far more justice by working with journalists towards a proper article than by blowing them off. It requires more effort, to be sure, but more accurate coverage of these incidents can help dispel the image of skydiving as a ruthless sport in which some participants die despite doing everything right.
Take the common statement of "The parachute failed to open," for example. This implies that the gear is at fault, when we all know that it's a very rare situation when the skydiver can do everything right and still die. Almost 100% of the time, a skydiver dies because of a primary (e.g., no pull, low pull, low turn) or secondary (incorrect response to a malfunction) mistake. The public doesn't understand this. While it might not seem important that they do, think of the number of times you are asked by non-skydiving friends and coworkers why you skydive, or hear a comment of how they can't believe you skydive, all with the overtone of why would someone want to do a sport that everyone knows will kill you. Do you get tired of that? I do.
The simple fact is that a large percentage of the non-skydiving population thinks that people who die skydiving die through no fault of their own, thus they think skydivers are a bunch of adrenaline junkies who don't care if they die skydiving. We know that's far from the truth, but when news articles don't give the whole story for long periods of time, this is the result. Additionally, it's frustrating to all of us skydivers when the story isn't right.
Following are some suggestions for dealing with the media in the event of a skydiving incident. Thankfully, most of you will never have to do this, but if you do perhaps this will help.
Send them to the source. If you are not the S&TA or other appointed drop zone media liaison, do not discuss the incident with a journalist. We all know that rumors bloom fast and furiously on drop zones, particularly in situations such as this. What began as a simple low turn by an inexperienced jumper on a smaller canopy than he was used to can quickly become an evasion of traffic, a dropped toggle, avoidance of an obstacle, etc., via the rumor mill. Whether you saw the incident or not, don't talk about it to the media and don't offer any opinions unless you're the media liaison. Refer any reporters to the S&TA or DZO, or whomever the drop zone has designated as the media contact. This person's job is no fun, but it's their responsibility to investigate the incident based on witness accounts and gear information, to prepare a complete report, and to deal with the media (and the coroner if the accident was fatal). Again, no one but the designated media contact should be talking to the media.
Don't dodge the press. We'll give chapter and verse to anyone who asks about most things related to skydiving, but when it comes to chatting with a reporter about a skydiving incident we often clam up. Why? Because we're afraid they'll get it wrong again. But if we don't give them information, we're guaranteed a minimal or misleading report of the incident. If we want these incidents to be reported accurately, the information has to come from us-the S&TA or designated media contact.
Be professional and courteous. Don't say, "You shouldn't be writing about this," because they will anyway, and this will just annoy the reporter and make it more likely that he/she will write something negative about the situation, the drop zone, and/or the sport. Also, it will burn a bridge that can be used for publicizing positive events at the drop zone such as charity events or milestones. Anytime you speak as a skydiver or skydive in front of non-skydivers, you are an ambassador for the sport whether you like it or not. Use this interaction with the media as a chance to portray skydiving accurately, and in the best light possible in a bad situation, by being honest and helpful. Avoid the "us vs. them" kind of interaction; this doesn't have to be a challenge where either you or the reporter gets their objective at the other's expense.
Think about your description beforehand. In all likelihood, reporters won't be there right away following an incident, unless it occurs during a demo. In either case, coverage of the incident will turn out better with better information, and you will be able to give better information after thinking about the incident a bit and getting it clear in your mind.
Be specific, but simple. It's pretty clear by now that I'm asking for more accurate reporting of skydiving incidents, and this isn't a problem for skydivers. What is more of a problem, especially if we're distracted by the substantial emotional impact of the incident, is that we'll talk to a reporter in the same way we'll talk to fellow skydivers-discussing things in skydiving terms rather than lay terms--if we talk to them at all. This doesn't improve the coverage, it just makes their eyes glaze over. For example, don't say "The right toggle came unstowed from the toggle tip keeper, allowing the cat's eye to come off of the loosely stowed brake and sending the canopy into a left-hand spiral to the ground," Instead, think about your audience (the general public as well as the reporter) and say, "It appears that a minor malfunction during deployment caused the parachute to spiral down, and so and so did not correct it in time to avoid the hard landing from the spiral."
Refer questions about a jump plane crash to the National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB). It is extremely counterproductive to speculate about the cause of a jump plane crash without an investigation report. If you are asked about a jump plane crash, refer reporters to the designated NTSB public affairs officer once he/she has arrived on the scene. We don't like it when uninformed reporters speculate about the causes of skydiving accidents, and the pilot (if he survived) and his family won't appreciate uninformed speculation about the plane crash either.
Offer to review the article before publication. It's not often that you will get the opportunity to do this, but you might if you offer it. What better chance will you get to ensure that the coverage is accurate? Of course, the reporter will reserve the right to accept or reject your changes as they choose, but the chance to review the article before publication is something not to be turned down.
The relationship between skydivers and the media has not always been a good one in general, as is often the case when laymen try to describe technical pursuits. That can't be changed overnight. But things won't get better without a responsible effort from both sides, hence the two-part coverage of this topic directed to both groups. A better working relationship between skydivers and the media, both for good and not-so-good events, will benefit both of us.
If you found Part 1 of this series useful-"Skydiving Incident Reporting for Mass Media Reporters"-please feel free to copy it and give it to any media representatives (print, web, or television) whom you think would benefit from it.
Sidebar: Recommendations for Working With Police
Working with the police in the aftermath of a skydiving incident is about as much fun as dealing with the press, but there are a couple of things they should know about the investigation that will make things easier for everyone.
First of all, the gear is only to be removed from the area by the coroner, not the police or the local rigger. When the coroner gets there, the drop zone representative and hopefully a rigger should be there to help answer any gear questions.
Most policemen don't know how to investigate the gear or scene, so removing evidence (gear) hampers the ability of those skilled in accident investigation-the coroner and your S&TA, rigger, or whoever is designated to investigate-to determine what happened. If the police want to rope off the area without disturbing the scene, that's fine. But if they try to remove the gear without it being investigated by the coroner, politely advise that they will get far more information if they will wait until the coroner, along with the S&TA or rigger, can inspect the scene and the gear with them. Don't get angry with them-which is easy to do when a member of our skydiving family has died and the police and/or media seem to be handling things wrong. Anger will only introduce further tension into an already awful situation, and make it less likely that things will get handled with skydiver input.
When the coroner is finished with the gear, the police often will impound it, do whatever they need to do with it, then release it to the FAA. The FAA then will usually inspect the gear with a rigger of their choice as part of an investigation.
Working with instead of against the police can help us get better answers to a skydiver's death than a feud. Make every effort to keep things civil and helpful, and this unpleasant situation will be minimally unpleasant for all concerned.
Thanks to Randy Connell, S&TA, S/L I, AFF I, for his contributions to this article.
Christy West is a journalist and gold/silver skydiving medalist with over 1,800 jumps.
Choosing Emergency Contacts
One of the things that all most every Dropzone or Boogie waiver has is a space to list an Emergency contact. Most jumpers just fill this information in with the first relative or friends name that pops into their head as they fill out the waiver, but jumpers should fill this section out after carefully selecting a contact. Jumpers should put more thought into this decision then they do into what type of jumpsuit they are going to buy.
There are criteria that make people better emergency contacts then others and jumpers should keep this in mind as they make their selection. Potential emergency contacts should meet the following criteria at a minimum:
Potential emergency contacts need to be aware of any medical issues or conflicts that you might have. If someone is allergic to something and forgets to put it on their waiver the emergency contact might just be the last line of defense there is to prevent the emergency responders from giving them a potentially dangerous drug or drug combinations.
Emergency contacts should have phone numbers to your immediate family members rapidly available so they may inform your loved ones about any potential incidents that might have happened. Poor choices for emergency contacts include people that have never met you or your family before you visit the DZ. At a minimum your emergency contact should have the phone number to contact the person that you would want to be notified of your injury or death first.
Another trait that makes a good emergency contact is choosing someone that is not at the airport the same time you are. In the case of something like a plane crash or canopy entanglement you might be involved in the incident with potential emergency contacts. By choosing someone that is not involved in skydiving or at the airport at all you maximize the availability of contacts that DZ personal might be able to reach in the case of an emergency on the dropzone.
Contacts should be someone that will be able to initially handle receiving potentially devastating news about you. Choosing someone that is known to be extremely emotional over the phone might be a poor choice as a contact if the Dropzone or medical teams need to ask questions of the emergency contact. Choose someone that will be able to calmly answer any potential questions after being informed that you are injured or worse.
Having multiple methods of contacting emergency contacts makes the task of reaching the emergency contact a lot easier for the dropzone personal. Emergency contacts should have at least one phone number and if possible multiple phones. List every phone number in the order that they should be called. Listing mobile numbers, home numbers and work numbers should all be done at a minimum to insure the maximum possibility of reaching someone in a true emergency.
Other things that should be used as criteria in potential emergency contacts include knowing who might be on vacation and out of reach at the time of certain boogies, knowing which contacts will be available to rapidly travel to deal with incidents if they happen, and in the case of international jumpers knowing the time difference and how that is going to affect the ability to contact your potential contact.
Using these criteria to choose an emergency contact will increase the probability that the dropzone personal will be able to reach and inform people of emergencies involving you, plus it will reduce the anxiety factor on the dropzone staff side in contacting people if they know they will not have to end up calling 10 people to reach someone that has needed answers about you.
Exit Emergencies
Exit Hazards-static Line
When climbing out onto a step for a S/L exit, you need to firmly plant your feet on the step so that you don’t trip over yourself and fall off. If you do find yourself prematurely exiting the aircraft, merely arch hard for stability. Don’t grab the pilot chute or parachute as it comes by you. To do so may cost you your life.
Exit Hazards-AFF
When climbing out for an AFF exit, your jumpmasters are supposed to have good control of you. If you start to stumble, they will probably help you into position. If you do prematurely exit, at least one of them should have a hold of you and you will need to arch hard for stability.
When climbing out, make sure your hands stay away from the jumpmaster’s ripcord handles. Occasionally a jumpmaster is launched off the step when a student grabs for the jumpmaster and snares a handle by mistake.
Dangling Static Line
After the jumpmaster dispatches each student, he will unhook the static line and stow it in the back of the aircraft or under the pilot’s seat. If he forgets to disconnect the static line, it is one ingredient for another horror story. During the scramble to exit, jumpers have managed to get those long pieces of webbing half-hitched around their ankle. The result is a surprising and abrupt halt just a short distance out the door. Due to the weight of the gear and the wind, it is impossible for the jumper to climb back up. There should be a knife in the plane to cut you loose and, of course, every experienced jumper in the plane should be carrying one. If there aren’t any knives handy, you will hope the pilot is sharp enough to think of breaking some glass out of one of the instruments in the panel because your alternatives are not terribly pleasant. Either you can pull your ripcord and risk jerking your leg off, or you can wait it out and suffer severe runway rash when the plane lands. One jumper caught in this situation lucked out, he was jumping a helicopter. The pilot set him down gently and red faced in front of everyone on the DZ.
Student In Tow
One of the more dramatic problems is the static line hang-up or student in tow. It occurs when you or some part of your equipment entangles with the static line preventing separation. You wind up suspended about ten feet below the aircraft by the long nylon web. This emergency is extremely rare and if it does occur, it will probably be because the static line is misrouted (perhaps under the harness). Maybe the error was missed in the equipment check, or you and the jumpmaster failed to keep the line high and clear as you moved into the door to jump, or you performed some wild gymnastic maneuver instead of a stable exit and became entangled in the line. Some students, despite all their training, yell arch thousand and then let go with the hands, leaving the feet firmly planted on the step, thus they perform a backloop upon exit.
The in-tow/hang-up situation presents all of you with a perplexing situation. The jump ship will be more difficult to fly. In fact, the pilot may be unable to maintain altitude because of all the extra drag. Just as with the dangling static line situation, you do not want to pull the reserve or land with the plane. As with other emergencies, there is an accepted procedure. You, your jumpmaster and pilot must be familiar with it.
The pilot will be diverting the aircraft to a safer, open area and will be trying to gain altitude. If you relax, you will probably assume a stable towing position either face or back to earth which is better than twisting in the wind.
If you are conscious and your arms have not been injured, signal the jumpmaster by placing both hands on top of your helmet. Your hands will show you understand the situation and are ready to take corrective action. Your jumpmaster will signal he is ready too by holding up a knife. Now, your jumpmaster will cut the static line and you will fall away. Pull the reserve ripcord. Be sure you are cut loose before you pull.
If you are unconscious or otherwise incapacitated, you won’t be able to give the OK signal to your jumpmaster. Your static line will still be cut but your jumpmaster (and you) will rely on your automatic activation device to deploy your reserve parachute.
Back when reserves were worn in the front, jumpmasters could lower an unconscious student by unhooking their own reserve and attaching it to the static line. The static line had to have an extra ring for attachment to the reserve to make this method of rescue possible.
There is also a second type of main canopy in-tow emergency to be considered. Normally, you fall away from the step so quickly that it is virtually impossible to tangle your canopy in the tail, but if one of your parachutes opens when you are on the step, entanglement may occur. If you find yourself in this situation, look up and determine which parachute is fouled on the aircraft. If it is the main parachute (which will be attached to risers that can be disconnected from the harness), look at your reserve ripcord handle, jettison your main and pull your reserve ripcord immediately, per the procedures that you were taught to use.
If it is your reserve that is entangled on the aircraft, pulling the reserve/SOS ripcord would not change your situation but it will make your main canopy useless as it would be disconnected at the risers, therefore don’t pull the reserve ripcord handle. The fouled canopy may just self-destruct, putting you back into freefall, in which case you will need to deploy your main parachute to save your life. (If you deployed your main parachute while the reserve is fouled on the aircraft, you can assume that major structural damage will occur to that aircraft and anyone left inside that aircraft will have to perform their own emergency procedures.)
Static Line Not Hooked Up
Occasionally, despite all procedures, a student exits the jump plane without being attached to it. While hooking up the static line is the jumpmaster’s responsibility, you must verify that it is attached prior to exit. If you forget to check this and find yourself in freefall, follow the procedure for a total: pull your reserve ripcord.
Pulling High Is Dangerous
Everyone else expects you to pull below 3,000 feet. If you pull higher, another freefalling skydiver could hit you. An open canopy descends at about 1,000 feet per minute and jumpruns are usually a minute apart. If you plan on pulling higher announce your decision to all before leaving the ground.
Canopy Emergencies: Breakaway
Jettisoning The Main Canopy
Before we talk about the series of problems you may encounter with your main canopy, it is important to discuss the types of cutaway (main canopy disconnection systems) that are in common use and their procedures. The breakaway or cutaway is an emergency procedure that involves jettisoning the main canopy prior to deploying the reserve. Originally, the cutaway was performed with a knife and the lines were cut to separate the canopy from the harness. Today, we use canopy releases to breakaway. The breakaway procedure should be executed immediately under rapidly spinning malfunctions because ever-increasing centrifugal forces will make arm movement difficult, and may cause you to lose consciousness (red-out) due to the blood flow to your eyes.
The decision altitude for the breakaway is 1,800 feet. This is your safety margin, above this it is safe to try to clear the malfunction but at this point, all clearing work must stop. Watch your altitude. The breakaway must be commenced above 1,600 feet to assure you plenty of time to get the reserve out. Under high-speed malfunctions, you may be just seven seconds off the deck at this point, and it may be necessary to forget the breakaway and just pull the reserve.
To breakaway, spread your legs (for lateral stability and push them back as far as possible while bending your knees about 45 degrees (only). Arch your back and pull your head back but keep your chin resting on your chest and your eyes on the handle(s). On release you will fall into a stable, face- to-earth position.
Body position during the breakaway is very important. If you are not falling away correctly, you may become entangled in the canopy and/or lines of your deploying reserve. Even with good body position, breaking away from a violently spinning malfunction may throw you tumbling across the sky.
The breakaway procedure is as follows:
Two Action System(TAS)
The TAS has two handles: Pull the first one (usually a Velcro-attached pillow handle located on the right-hand main lift web), to release both risers (a single point release). Then activate the reserve by pulling the other handle (usually located on the left-hand main lift web).
A. Total malfunction (nothing out)
Do not waste precious time breaking away; just pull the reserve.
LOOK at the reserve ripcord handle and arch.
REACH for the reserve ripcord handle with both hands.
PULL the reserve ripcord handle with both hands.
B. Partial malfunction (canopy out but not working properly)
There are two schools of thought on how to perform the breakaway action using this system. The first one presented is in the USPA’s Skydivers Information Manual, “Section 8-3.16.” While it states “Look at the reserve ripcord handle...” (step 3), it says nothing about the choice of one hand or both on the breakaway handle. It is as follows:
LOOK at the breakaway handle and arch. The arch should keep you from making a backloop when you jettison the main.
REACH for the breakaway handle (presumably with both hands).
LOOK at the reserve ripcord handle before breaking away.
PULL the breakaway handle and throw it away while continuing to keep your eyes on the reserve handle.
REACH for the reserve handle with both hands.
PULL the reserve ripcord.
CHECK over your shoulder for a pilot chute hesitation.
CHECK your reserve canopy, look around and prepare to land.
Note: For student equipment, and something that is becoming more popular on experienced jumper equipment, there is a device known as a reserve static line lanyard RSL (sometimes called a Stevens lanyard). This is a piece of webbing attached from the right side riser (or both risers on some systems) to the reserve ripcord cable. It is designed to pull the reserve ripcord out of its locking loop(s) as you fall away from the main parachute after that main canopy is cut away, thus allowing the reserve to deploy. When installed and operating properly, it will usually beat you to the manual deployment of the reserve. However, it should not be relied upon, for after all, along with an automatic activation device (AAD — described in Chapter 7), it is merely a back-up device to your proper execution of emergency procedures. This system can be disconnected (if necessary) by personnel who know what they are doing.
It is a possibility that when you perform a breakaway using both hands on the breakaway handle, there is a fraction of a second of disorienting instability as the maneuver is executed. Although you are supposed to be looking at the reserve ripcord handle, you still need to move one or both hands to it from whatever position you are in at the conclusion of the breakaway-handle pull. The ripcord handle may move from where it was (on the harness) under the tension of the partial malfunction to a different position during this moment. It is a possibility that there may be an additional second or more of elapsed time as you reach for the reserve ripcord handle.
Therefore, there is a second school of thought about performing the breakaway, which is, if you are about to execute a breakaway and you put your right hand on the breakaway handle and your left hand and thumb through the reserve ripcord handle, there will be no lost time reaching for the reserve ripcord after the breakaway is executed. Here is a typical scenario:
LOOK at the breakaway handle and arch. The arch should keep you from making a backloop when you jettison the main.
REACH for the breakaway handle with your right hand.
REACH for the reserve ripcord handle with your left hand, placing your thumb through the handle to ensure that you have a firm grip on it.
PEEL and PULL the breakaway handle to full right arm extension. Throwing it away is optional.
Immediately after you’ve pulled the breakaway handle with your right hand, PULL the reserve handle out to full extension with your left hand.
CHECK over your shoulder for a pilot chute hesitation.
CHECK your reserve canopy, look around and prepare to land.
In this scenario, there is no hesitation in looking for a reserve ripcord that may have moved, thus it may save a second or two of precious time.
The Single Operation System (S.O.S)
The Single Operation System is a one-handle/one-motion system. The S.O.S. has a combined handle, usually on the left main lift web, to release both risers and activate the reserve. The S.O.S. has a reserve static line lanyard (Stevens lanyard) from one riser to the reserve ripcord. The purpose of the S.O.S. is to eliminate one the motions in the breakaway sequence; that of separately pulling the cutaway handle. By pulling the reserve ripcord all the way, you accomplish both the breakaway and the reserve-ripcord pull in one complete action. With a two-action system, half a breakaway is worse than no breakaway at all unless you have an RSL.
The S.O.S. usually produces full deployment of the reserve canopy in less than 100 feet. If you find an RSL on your piggyback harness/container assembly, you should leave it on. When you and your instructor develop enough confidence that you will pull the reserve after a breakaway, you can do away with the line if you wish.
Total or Partial malfunction
In the event of a total or partial malfunction:
LOOK at the combination release/ripcord handle and arch.
REACH for the combination handle with both hands.
PULL the combination handle with both hands to full arm extension.
REACH back with one hand, grasp the cables where they come out of the housing.
PULL AGAIN to clear the cables and
CHECK over shoulder for a pilot chute hesitation.
CHECK the reserve canopy, look around and prepare to land.
Never depend on the reserve static line device (Stevens lanyard). Always pull your reserve ripcord cable all the way out of the housing immediately after breaking away.
Canopy Transfer
Canopy transfer is a third type of breakaway procedure sometimes used in Canopy Relative Work by those who believe something is better than nothing. If your main canopy becomes damaged or tangled on a jump and it is still flying forward, you may pull your round reserve and drag it behind you, full of air. Once the reserve canopy is inflated, jettison the main. This maneuver is extremely risky with a square reserve canopy as two squares may fly around and into each other. This type of problem is discussed later on in detail.
Harness shift
When you jettison the main canopy, your harness will shift downward taking the reserve ripcord location with it. Therefore, it is essential that you keep your eyes on the reserve ripcord handle, if your hand is not already grasping it, when jettisoning the main canopy.
Now that we have covered cutaways (breakaways), let’s discuss when and where they are used.
Landing Challenges
Most of your landings will be normal and in the center of the drop zone, but unusual things do happen like landing in water, in sudden high winds, descending through power lines or trees.
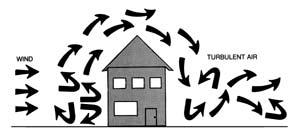
Turbulence
As mentioned earlier, bumpy air may be encountered at any altitude and it has been known to close end cells and upset canopies. Jumpers have been robbed of their wings to be left back in freefall at 75 feet. Bumpy air may occur on windy days and on hot, no-wind days. Keep your canopy inflated during turbulence by flying at one-quarter to one-half brakes and make gentle turns. If turbulence causes a partial canopy collapse of your canopy, bring the steering lines down to half to
three-quarters brakes to help the canopy to reinflate.
Turbulence near the ground may be caused when wind flows over obstacles such as buildings and tree lines. Avoid landing on the downwind side of any obstacle. The air may be bumpy or descending. The stronger the wind, the farther downwind the turbulence will exist and the taller the object, the higher the turbulence will be. Turbulence can be significant downwind as far as twenty times the object’s height. For a fifty-foot tree line, that could mean 1,000 feet downwind turbulence.
Turbulence also occurs behind other ram-air canopies. Stay away from the area directly behind another canopy about 45 degrees up from the trailing edge.
Dust Devils
Dust devils are very dangerous. They can rob you of your canopy when you need it most — near the ground. Look for the spinning dust clouds. Unfortunately they can’t be seen over grass.
One jumper landed, his canopy deflated and then it was reinflated by a dust devil. The swirling wind picked him up and then threw him back on the ground. He died from the impact. In windy conditions, pick up your deflated canopy immediately. In bad conditions, stand on it.
High winds. If you find yourself in high winds, look behind you as you back up. Many jumpers back into power lines and fences. When landing in high winds, let go of one toggle as soon as your toes touch the ground. Keep the other toggle at the flare position and quickly pivot 180 degrees in the direction of the depressed toggle. Steer the canopy into the ground. Run toward and around it to collapse it. If necessary, continue pulling on that toggle and reel in its line to pull the canopy out from under itself.
Once you are on your feet, stand on the canopy and remove your harness. Don’t let it reinflate and start dragging you all over again.
Thunderstorms
Thunderstorms are violent vertical lifting of air masses, a phenomenon which can build cumulonimbus clouds from near the ground to anywhere from 50,000 to 75,000 feet. Thunderstorms possess violent updrafts and downdrafts along with lightning. While the West Coast of the U.S. has only around five thunderstorms each year, the northeast has 20, and Florida 80 to 90. Jumpers have been caught in cumulonimbus clouds for some pretty scary and wet rides. When the storm clouds appear, put the gear away.
The Tree Landing
The tree landing is rarely hazardous if you “center” the tree. Your canopy will lower you gently into and through the trees as you slow further, breaking the thinner branches. You will probably go all the way through to the ground and make a normal parachute-landing fall on
the other hand, if you clip a tree with a wing tip, your canopy may collasp, dropping you to the ground.
If you can’t avoid the trees, face into the wind to minimize your ground speed, pull half brakes, and place your feet and knees tightly together so you won’t straddle a branch. Do not attempt to brake your descent by grasping limbs; you are better off going all the way through to the ground slowly than ending up sitting in the top of the tree. Prepare for a PLF. If you come to rest short of the ground, check your position. Students should wait for DZ personnel to come to their aid.
If your feet are within three feet (1m) of the ground, unfasten your chest strap and then your (solid saddle) leg straps and drop to the ground. If you do not undo the chest strap first, you could injure your neck as you fall away.
If you are up quite a way, relax and wait for help. If help does not arrive, you may have to climb down. Perhaps you are way off the DZ and dusk is approaching. It’s hard to shout continually, and it is nice to have a whistle in times like these. You may deploy the reserve canopy without activating the cut away mechanism (for S.O.S. type equipment, pull the metal cable out of its housing without disturbing the plastic-coated breakaway cables), let down the canopy and lines and then climb down hand over hand. If you let the narrow lines slip through your fingers and aren’t wearing gloves, you will receive painful friction
burns, so go hand over hand.
Keep your helmet on until you have both feet firmly on the ground. Its purpose is to protect your head from takeoff to touchdown, and you aren’t down yet.
Power Lines
You must avoid power lines at all cost; the danger is just too great. Look for the high-tension wires. If you are at an unfamiliar DZ or land off target, look for poles; wires run between them invisibly. Keep power lines continually in mind from the time you open so you can avoid them. High-tension lines don’t look dangerous, but they strike with the speed and power of lightning. They may electrocute you in an instant or put you in the hospital with severe burns; it isn’t at all pleasant. If there is any question about clearing the lines, turn and run with the wind until you are past them and make the decision high enough. It will be better to land downwind than to land in power lines.
If landing in the wires is inevitable, it is essential that you avoid touching more than one wire at a time. Any bird will tell you that it takes touching two wires to get zapped. If you are going into the wires, face your canopy into the wind to minimize horizontal drift, pull half brakes to make your final descent as close to vertical as possible. Drop your ripcord or anything else in your hands. Place your feet and knees firmly together with the toes pointed to avoid straddling a wire. Look for wires and wriggle and squirm as necessary trying to avoid touching more than one at a time. If you come to rest near the ground, check below to see what is underneath you. If there is no hazard below you and it is less than five feet to the ground — and assuming it is the main canopy that is hanging you from the wires you might decide to execute a breakaway and get away from the danger area as quickly as possible, but it would be better to wait for calmer heads to give you guidance in this matter. If there is a hazard below you or if it is your reserve parachute that is hanging you from the wires, you must wait calmly for competent, professional help. Any movement on your part may force an electrical contact. If a local resident walks up desiring to help you, ask them to call the power company and the DZ in that order. Warn would-be rescuers not to touch you or your gear until the power has been turned off. They could complete a circuit between you and the ground with fatal results.
Once you get to the ground, be alert for broken power lines, they are like snakes hidden in the grass and they not only strike, they sometimes start fires. Never pull on a canopy attempting to remove it from the wires, it may be your very last good deed. Let the power company do it; it is their kind of work.
Water Landings
There are two types of water jumps — those you plan and those you don’t. An intentional water jump is an exciting, rewarding combination of aviation and water sports. But being unexpectedly blown out over a body of water is cause for great concern. In fact, while few jumpers have perished in a planned water jump, 48 perished in unexpected water landings between 1967 and 1984. These figures have dramatically decreased now that the use of ram-air canopies has become universal and floatation devices for operations within one mile of water are mandated by the BSRs.
The procedures for these two very different types of landings are not the same.
In an intentional water landing you will slide back in the saddle, undo the chest strap, the bellyband (if there is one), and loosen both leg straps slightly (unless you have a full saddle harness, in which case you can release one leg strap up high, then the last leg snap upon splashing down). This procedure is also recommended if you find yourself being blown unexpectedly out over the ocean or other immense body of water. When there is absolutely no question that you are going for a dunking, you should inflate your floatation device. Don’t get out of your gear until you get wet. Don’t break away when you think you are about to get wet. Depth perception over water is deceptive. You may think you’re at 20-feet, but you’re probably much higher. Without knowing how deep the water is, you almost guarantee yourself a landing injury if you don’t steer the canopy all the way to the surface. For landing purposes, assume the water is just a few inches deep. Take a deep breath and prepare to do a PLF. Line up your landing into the ground winds (you may have to use the sun’s position for a reference) and once you are wet, swim or work your way forward out of your gear. Don’t try to save the gear at first. Remember that it is replaceable, you aren’t. Worry about the gear later, when you are safely away from it. Better yet, let someone else (such as your water landing crew) worry about it.
When making an intentional water jump, conditions are good, the jump is planned and the necessary flotation equipment is worn. The ingredients for tragedy, on the other hand, are born by being unprepared for the unexpected.
The Basic Safety Requirements insist on carrying flotation gear when parachuting within one mile of any water deep enough to take a life, but there are times when one mile is not enough. A bad spot on a big load with high upper winds, sudden radical wind changes, or a popped round reserve as you exit at twelve grand, for examples, may carry you far from the friendly DZ. Some water requires more protection than just flotation gear, such as when a jumper punches through the ice in the wintertime.
Most unintentional water landings are also unexpected. They take place in narrow rivers and small ponds; so small that you don’t know you are going into them until just a short distance from splashdown. There is no time to do much water-landing preparation, particularly if you are trying to avoid trees. As a result, you are going into the water in all your gear and your chances are poor.
On the other hand, if you go through the intentional water landing procedure just in case and then miss the water only to land in the trees because you couldn’t spend enough time steering, you may subject yourself to other dangers.
The greatest danger in water landings is becoming entangled in the net-like canopy and lines. In fact, we should think of: panic-canopy-entanglement-drowning. All are challenges, very much related, and either of the first two can lead to the others. If there is little wind in the small tree-protected pond, the canopy will deflate and fall straight down on you in a huge mess of tangled nylon fabric and lines. If you panic, you are sure to become caught in the trap. It seems logical, then, to try to avoid the canopy, or better yet, avoid the water landing.
The procedure recommended for unintentional water landings is as follows: You are at 1,000 feet and the wind is backing you toward a water hazard. If you continue to face the wind, you may land short of it and if you turn to run, you may land on the other side of it, but one thing is for sure: you will land in the vicinity of it. So, take the action outlined below and then at double to triple the height of the trees, face into the wind to minimize your ground speed, pull your
toggles to half brakes, and place your feet and knees firmly together in preparation for a PLF.
Two Action System (TAS)
Continue to steer, activate your flotation gear if you have it, undo your chest strap and your belly band if there is one. Loosen your leg straps so that you can slide the saddle forward a bit. Disconnect the RSL. Then, just before touchdown, reach for the canopy release handle. At the moment your feet get wet, not one moment sooner, activate the releases. The tensioned canopy will recoil upwards and even a mild wind will carry it away. Altitude is very difficult to judge, especially over flat ground or a large body of water. One is always tempted to drop out of the harness just before touching down, but what appears to be just a leg length may really be building height, so don’t break away until your feet are in the water.This procedure will leave you floating with your harness and reserve on but with the dangerous unpacked main canopy gone. Roll over on your back and take off the harness. Actually, the harness won’t hurt or restrict you and the packed reserve will even provide positive flotation. In fact, the reserve won’t become negatively buoyant for about three minutes. So, you can use it for temporary flotation.
Single Operation System (S.O.S.). With the S.O.S. system, if you jettison the main canopy, the Stevens lanyard will activate the reserve. Allow yourself to get wet, bend forward and then swim or work your way forwards out of the loosened leg straps as quickly as possible. Get clear of the canopy.
If the canopy does land on top of you anyway, grab it and follow/walk a seam to the edge of the canopy. There is no reason to panic as you can always lift the porous fabric to form a space to breathe. Once clear of the canopy, swim away using mostly your hands until you are clear of the lines. Keep kicking to a minimum, as pumping legs tend to draw lines and fabric toward them.
If you should land in a river, even a slow moving one, you want to jettison your main as soon as possible. If it catches in the current it will drag you under and/or downstream away from your rescuers.
Besides your reserve, certain other pieces of your gear may provide some flotation. Pneumatic soled jump boots, full shell helmets, knotted jumpsuits, etc.; they are all there for those who think to use them.
You must undergo (dry) unintentional water-landing training for your USPA A license and (wet) live water training with full gear for the B license. These requirements have probably saved hundreds of lives so far.
Buildings
Landing on a building presents two distinct hazards. First, you might go through the roof of the building, which may lead to a broken or cut extremity. Second, if it is windy, you might find yourself being dragged off of the building and going for a second extremely hazardous landing. If you feel your life is in danger (such as being dragged off a high building), break away from the main as quickly as possible. Don’t worry about the reserve inflating — it won’t have enough of a
chance to do so. If it is your reserve that put you on the building, try to collapse it as quickly as possible. If that doesn’t work, you’re going off the building in the wrong position for a second landing and there probably won’t be much of a chance to get into a PLF mode, but try to anyway.
Other Obstacles
There are many other landing obstacles that are potentially hazardous to parachutists such as ditches, fences, hard roads and even some unique ones like hot water geysers. These hazards at your DZ will be pointed out to you in your first jump course, probably with a marked aerial photograph. When visiting a new drop zone, be sure to check in with an instructor or the Safety & Training Advisor for a briefing on their local hazards and recommended alternate landing areas.
When you are in the air, look for the danger areas. Invisible
barbed wire runs between visible fence posts, power lines run between power poles, isolated buildings are served by electricity. Power lines, ditches, and fences often border roads, airplanes land on runways, etc. This should all be obvious, but sometimes it’s not. It is all new to you and the view is different: you are looking down at the terrain now, not horizontally.
If an obstacle presents itself, steer your canopy to avoid it. Turn your canopy to run and land beyond it, if necessary. If you are going to strike an object, hit it feet-first. Successful landings under a parachute are like those in an airplane: the ones you walk away from are good. It is far better to land outside the target area and walk back than land on a fence and be carried back. Don’t let get home-itis get you. If you pass over the obstacle very low, you may not have sufficient altitude to turn into the wind for landing. It is then preferable to crab the canopy slightly and try to do your best forward PLF. But, obviously, the best solution is to think and plan ahead to avoid the obstacle in the first place. The most important rule about landing hazards is: Continually make efforts to avoid them. The second rule is: It is better to land flying downwind than to hit an obstacle.
Freefall Emergencies
Accelerated FreeFall (AFF) Emergencies
As you get ready to leave the aircraft, you are supposed to do a pre-exit check to make sure that your jumpmasters are ready to exit too. If you make an error in your exit count, you can fool your jumpmasters (JMs) into thinking that you are about to leave and they may end up pulling you off the aircraft before you are truly ready to go. If you leave at the wrong time in the count, you could be taking your jumpmasters in tow. This could lead to some awkward flying if you are not arched. You may be positioned in a reverse arch (like a cat standing on top of a toilet bowl) which will attempt to send your butt to earth. The exit timing depends upon you doing the exit count right so that your jumpmasters can exit with you, not before or after you. If you find yourself looking up at the sky or tumbling, arch hard for stability. Your jumpmasters will be doing their best to assist you in getting back to the proper belly-to-earth position.
AFF:Loss Of One Jumpmaster
If you sheared off one jumpmaster during the exit or one let go because he was not contributing to the stabilization of the formation, arch for stability and check with the remaining jumpmaster during your circle of awareness. If you get a headshake of “NO,” it may mean that the jumpmaster holding onto you is not quite comfortable with your stability at that time. On the other hand, it may mean that he doesn’t want you to go to the next portion of your tasks because the other jumpmaster is just about to re-dock on the formation and he wants that jumpmaster in the correct position before you continue with your tasks. You may or may not feel the other jumpmaster re-dock. Whenever you get a “NO,” simply arch a bit more, wait a few seconds, then do another circle of awareness. If you get a nod of “YES,” you may continue on with your skydiving tasks regardless of whether or not you have just one of both jumpmasters firmly holding onto you.
AFF: Loss Of Both Jumpmasters
You are in an extremely hazardous environment if you don’t have a jumpmaster holding onto you. The moment you realize this, arch and pull immediately.
The following emergencies apply to either AFF or S/L program freefalls. Of course, in the S/L program, a jumpmaster might not be in the air with you during your freefall.
Five-Second Rule For Loss Of Stability
Here’s a good rule for AFF or freefall. It is called the Five-Second Rule. If you are out of control, attempt to regain control by arching hard for five seconds. If you don’t recover stability by the end of that five-second period, pull your ripcord immediately (which one depends upon your altitude). This rule is normally taught to AFF students when they start their Level III training and it is applicable to all freefall students.
Loss Of Altitude Awareness
If you can’t determine what your altitude is because you can’t see your altimeter and you can’t see either of your jumpmasters’ altimeters, arch and pull immediately. The worst of all situations is to go into the ground at a high rate of speed simply because you didn’t know where you were.
Goggles
If your goggles weren’t tight, they may come up off of your eyes and cause sight problems. You could simulate a practice pull position and try to hold them in their proper place, but it is probably better to end the freefall once the situation occurs. There is nothing worse than a distraction to disorient you and cause you to lose track of time and altitude. When in doubt, whip it out.
Briefings And Safety Considerations
Hazard Briefings
Emergency procedures will vary from drop zone to drop zone to fit local conditions. There may be trees, rivers, power lines, hostile neighbors, prisons, highways or a girls’ school. In fact, those DZ’s lacking certain hazards may touch on the corrective action for every emergency but lightly. Therefore, when visiting a new DZ, it is imperative that you get a briefing on the area.
Alcohol And Drugs
In order to achieve the greatest enjoyment from your skydiving experience, you will want to approach it with an unfogged mind. This means going to bed early the night before and going easy on the booze. Even the common cold will trouble you due to the changes in atmospheric pressure. If your mind and body are not operating at 100%, you will react with less efficiency in an emergency and you will enjoy the jumping less. Remember, the lower pressure at altitude amplifies the
affects of alcohol and drugs.
Health Concerns
Jumping with a head cold can lead to ruptured sinuses and ruptured ear drums. The inner ear and the Eustachian tubes do not take kindly to large pressure changes when they are plugged. Infections in these areas can produce debilitating pain under normal jump conditions. In a few words — if you are sick or under the weather, don’t jump. Loading up on antihistamines and decongestants can cause other medical problems. There is always another day to enjoy a jump in good health.
Scuba Diving Alert
There is no problem in descending into the water within 24 hours of jumping or flying, however, there is trouble waiting in doing the reverse. Scuba divers know to stay away from air travel for a period of 24 hours after their last descent below 30 feet (one atmosphere’s increase in pressure) so as to avoid the bends (nitrogen bubbles forming in the joints and blood stream). Since skydiving involves air travel, the same rule applies.
Some Fear Is Good For You
It has been said that the difference between fear and respect is knowledge. Most people fear skydiving because they don’t understand it. Fear is the result of ignorance and it is part of nature’s protective mechanism; it warns us to beware when we are on unfamiliar ground. The best way to cope with problems is to prevent them in the first place. The key is education. It is unfortunate when someone is injured while engaging in sport, but it is tragic when a second person is hurt for the same explainable and preventable reason.
Leaving The Nest
You're off student status, you have your own gear, and you're ready to strike out on your own for a change of scenery. Here's what you can expect to find, and here are some things to know, when you go to a new dropzone. It's worth spending some time to prepare for your adventure.
Before Leaving Town
There are many sources for finding dropzones, online or in print. Before leaving town, look up all of the possible dropzones listed within a reasonable range of where you'll be going. Start be searchng the Dropzone.com Dropzone Database. You can also try the USPA web site or search on Google for the state+skydive. Don't forget to ask other people about places they've been. Also, just because a dropzone doesn't have a turbine-engine plane, don't rule it out of consideration. You often learn more in one day at a small dz, finding out or applying things that aren't emphasized at larger dropzones. Check that your gear is in good condition and that your re-pack and AAD are in-date; more dropzones require and check both of these items. Bring a camera to take pictures with the people you meet. You may also want to bring water and food, because not all dropzones have this on site and may be far from a nearby gas station. If in doubt, call ahead and find out the specifics.
Finding The Dropzone
Mapquest is a great way to find your way to the town where the dz is located, but it's usually up to the dropzone to provide the final details for finding the actual facilities - this is a hit or miss situation, when it comes to how accurate this information is. Some places assume that you live in the region and are familiar with the area - then you find that not all of the road signs are visible or even present. Not all of the local gas station clerks will know of the small airports in the area, much less the dropzone. Be sure to have the dz number handy but don't be surprised if the phone is busy, or if you get diverted to an answering machine during the weekend, so be prepared and have printouts of all possible directions. Look for signs to the airport outside the city, or the large orange balls on power lines - these are dead give aways! However, there are times when two small airports are close together, confusing matters for you. If you time things right, you'll find canopies in the air and loads of cars parked out front, covered with skydiving stickers.
What to do when you arrive at a new DZ
Manifest is the best place to start - and every good dropzone should have someone who's willing to help you get in touch with the right people, for a complete briefing of the landing area and dropzone "rules", as well as hooking you up with some of the local jumpers. Be open and ready to jump with people of all skill levels, plus both styles of jumping (Freeflying and RW) - the more limits you put in place, the more likely you'll be stuck doing solo jumps. Be ready to do some solo jumps, in case you don't get hooked up with other jumpers who are willing to jump with you or when no one else is available to jump that day. You must be the one to ask others to jump with you; after all, you are the new kid on the block.
At manifest, complete their waiver, get a gear check, and find a spot for your gear bag. Depending on the size and location of the dropzone, be prepared for anything, when it comes to the bathroom facilities. Get the scoop on jump tickets - How-much-to-how-much (cost/altitude). Check on the charging and refund policy on jump tickets; often there is a charge-card percentage fee, slightly raising ticket prices. Most will give a full refund of the ticket value, but not the charge-card fee. Some will not refund your jump tickets but they usually don't have and expiration date, so you can use them whenever you happen to return. Buy only what you need, depending on these policies.
Get the lowdown on the manifest procedure for getting on a load. Do you pay in advance, pay as you go, pay at the end of the day? Also, do they use monitors to show the loads, do they announce names for the loads, or do they assume you know the load number you're on when they call it? Is there a separate window for manifesting, or do you go back to the main office?
Get a briefing on the basics:
The exit-order and separation rules - some places have very specific procedures and rules on these, others leave it up to you and your skills - ask and watch others.
Landing area obstacles - in addition to buildings, power lines, bodies of water, and the local farmer McNasty, some places have well-known areas of turbulence, small but harmful ditches, hills, or slopes, and hints on landing patterns to avoid them. Most places have several landmarks they use to locate the landing area, like highways, rivers, or lakes that form visual arrows pointing in the direction to look. Ask what is considered a good vs/ bad spot, for that particular dz, and the landmarks used for estimating this from the plane. Always ask where the beer line is located, if they don't mention it to you first.
Hard Decks - Some dropzones have set a hard deck as high as 3,000 ft AGL, for good reasons. It doesn't hurt to check on this, especially when the landing area is tight and surrounded by trees, lakes, or densely developed land.
Outs - Most dropzones have a good selection of areas to land out, but it's up to you to always stay aware of your surroundings; look out the plane's windows from time to time, to locate the landing area and the open areas around it - check with others to be sure you're not looking at swamps or thistle fields.
The prevailing winds - some places have both tetrahedrons and wind socks but not all of them use both or will have rules on when to use which of the two wind indicators. Find out what is most reliable because tetrahedrons tend to rust and stick.
Landing patterns - these vary as much as the winds - ranging from the first-one-down sets the pattern (and hopefully into the wind), to always using a left or right-hand pattern, or no particular rule except to avoid others. It's best to stay clear of others when possible and land a little further from the main landing area..
Swooping and hook turns - each dropzone owner has the discretion of allowing hook turns and often have an area designated for this and or swooping. If there is no area for this, keep alert while under canopy and ask if the people before you are going to hook turn or not, so you know not to follow their landing pattern (if the first-one-down rules are used).
Loading the plane - If you're lucky, you can walk to and from the plane and landing areas; everywhere else will require a bus, van, or trailer to one or both of these areas. Find out where you need to go for any of these options and how the loads are announced, so you don't miss your call for boarding the bus to the plane or hold up the trailer back to the packing area.
Gear Check - few places have a set rule for jumpers to do gear checks for the person sitting next to them. Therefore, it will often be up to you to ask for this.
Ask a lot of questions. Ultimately, you're responsible for your actions and should know all that's necessary to jump safely.
Your First Jump
You may end up doing a solo "orientation" jump as your first jump. Hopefully that will be the only solo you do and use it to take a good look at what happens on jump run, while others are exiting, and the ground features when in freefall. Have in mind a jump and an exit you'd like to practice. This helps you feel more at ease with what to expect. When jumping with others, this avoids the conversational volley of questions, "Whadaya wanna do? I dunno, whadayou wanna do?" Keep it simple; you're likely to end up working on matching fall rates on your first jump. Be sure to agree on a break-off altitude that's comfortable for you and not the people who have done the last 200+ jumps at their home dropzone. If the plane is different from any one you've been in, ask for suggestions for the exit.
Depending on your home dz location, in some areas it's a good idea to wear gloves, especially for your first jump, so you don't freeze your hands or in the event you land out and your landing isn't so smooth, and your hands run into rocks or "other natural abrasives". Check that your altimeter is zeroed, your dytters are set, and your AAD is activated.
Gear check, gear check, gear check - touch all handles and check all straps, then check those of the people around you and ask for someone else to check yours before exiting. You're taking in a lot of new information, so make sure you don't overlook anything. You wouldn't be the first to mis-route a chest strap but it could be the last time you'd ever jump.
On your way to altitude, remember to look out the windows so you can familiarize yourself with the surroundings and look for the landing area. Have in mind your landing approach. If you're doing a solo, and you're not sure about spotting, don't be afraid to ask the person before or after you to check the spot for you. It's a good idea to pull high, (be sure to let manifest and the jumpmaster and others on the load know) in order to give you enough time to adjust to the area and to have plenty of altitude to make it to the landing area.
Keep your head on a swivel. You're in new territories and you want to make it safely back to the landing area - avoid aggressive canopy pilots, hopefully they'll be on the ground before you land. Elect to land in a distant, wide-open area, which has less traffic; then move in closer on the next jump, if you feel comfortable.
At larger dropzones, there's usually a "packer's area" - ask, so you're not getting in someone's way of making money. Sometimes, if you accidentally set your rig in a packer's area and leave for a drink, you'll come back to find a packed rig and someone asking for payment. Smaller dropzones may not have any packers, so be sure you haven't forgotten how to pack your own rig. Also, at larger dropzones, there are sometimes separate packing areas for belly flyers and free flyers - a strange and unfortunate thing, in most cases.
Your Next Jumps
Some dropzones have landing areas at a different altitude than the packing area, especially when a bus/van/trailer is involved in moving between the landing area and loading area. Make the necessary adjustments to your AAD, hand altimeter, and dytter settings.
When You Leave
If you plan to go to a second dropzone during the same day, turn off your AAD before leaving and turn it back on again at the next location. Also, take pictures with the people you jumped with that day and add them to your logbook. Don't forget to swap e-mail addresses when you can. Find out if the dropzone has a stamp to put in your logbook, almost like a customs stamp for your passport.
Where To Stay
There can be many choices or just your car, so be sure to ask what's available; again, manifest is a good place to start. Many places have something on site, ranging from a couch in the hangar to a full-fledged house with all of the trimmings, and ranging in price from free to something that's usually within the budget of an avid skydiver. If you made friends that day, the local jumpers may offer to let you stay at their homes, another good reason to jump with others and not sticking to solo jumps. If you're not satisfied with these options, then nearby hotels often have discounts for skydivers, be sure to ask before making a reservation.
Going to different dropzones is a wonderful experience and it's even more exciting when you go alone, seeing it through your own eyes and not through someone else's expectations. You see and do things differently than you would in familiar surroundings; this also keeps you from becoming complacent in this unforgiving sport. The people you meet become instant friends, if you let them, given the common bond of skydiving.
Karen Hawes has jumped at dropzones in all 50 US States, 4 Canadian Provinces, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Spain and The Bahamas.